Arduino - Horloge temps réel
Dans ce tutoriel, nous allons apprendre :
- Comment obtenir la date et l'heure (secondes, minutes, heures, jour, date, mois et année) en utilisant Arduino et le module horloge temps réel DS3231.
- Comment créer un emploi du temps quotidien avec Arduino
- Comment créer un emploi du temps hebdomadaire avec Arduino
- Comment créer un emploi du temps pour une date spécifique avec Arduino
Préparation du matériel
Ou vous pouvez acheter les kits suivants:
| 1 | × | Kit de Démarrage DIYables STEM V3 (Arduino inclus) | |
| 1 | × | Kit de Capteurs DIYables (30 capteurs/écrans) | |
| 1 | × | Kit de Capteurs DIYables (18 capteurs/écrans) |
À propos du module d'horloge en temps réel DS3231
Arduino possède en lui-même des fonctions liées au temps telles que millis(), micros(). Cependant, elles ne peuvent pas fournir la date et l'heure (secondes, minutes, heures, jour, date, mois et année). Pour obtenir la date et l'heure, nous devons utiliser un module d'horloge temps réel (RTC) tel que DS3231, DS1370. Le module DS3231 est plus précis que le DS1370. Voir DS3231 vs DS1307
Schéma des broches
Le module d'horloge en temps réel DS3231 comprend 10 broches :
- Broche 32K : fournit une horloge de référence stable (compensée en température) et précise.
- Broche SQW : génère une belle onde carrée à 1Hz, 4kHz, 8kHz ou 32kHz et peut être gérée par programmation. Ceci peut également être utilisé comme une interruption due à une condition d'alarme dans de nombreuses applications basées sur le temps.
- Broche SCL : est une broche d'horloge série pour l'interface I2C.
- Broche SDA : est une broche de données série pour l'interface I2C.
- Broche VCC : alimente le module. Elle peut être comprise entre 3,3V et 5,5V.
- Broche GND : est une broche de masse.
Pour une utilisation normale, il nécessite l'utilisation de 4 broches : VCC, GND, SDA, SCL.

Le module DS3231 dispose également d'un support de batterie.
- Si nous insérons une pile CR2032, cela permet de maintenir l'heure sur le module lorsque l'alimentation principale est coupée.
- Si nous n'insérons pas la pile, les informations horaires sont perdues si l'alimentation principale est coupée et vous devez régler l'heure à nouveau.
Diagramme de câblage
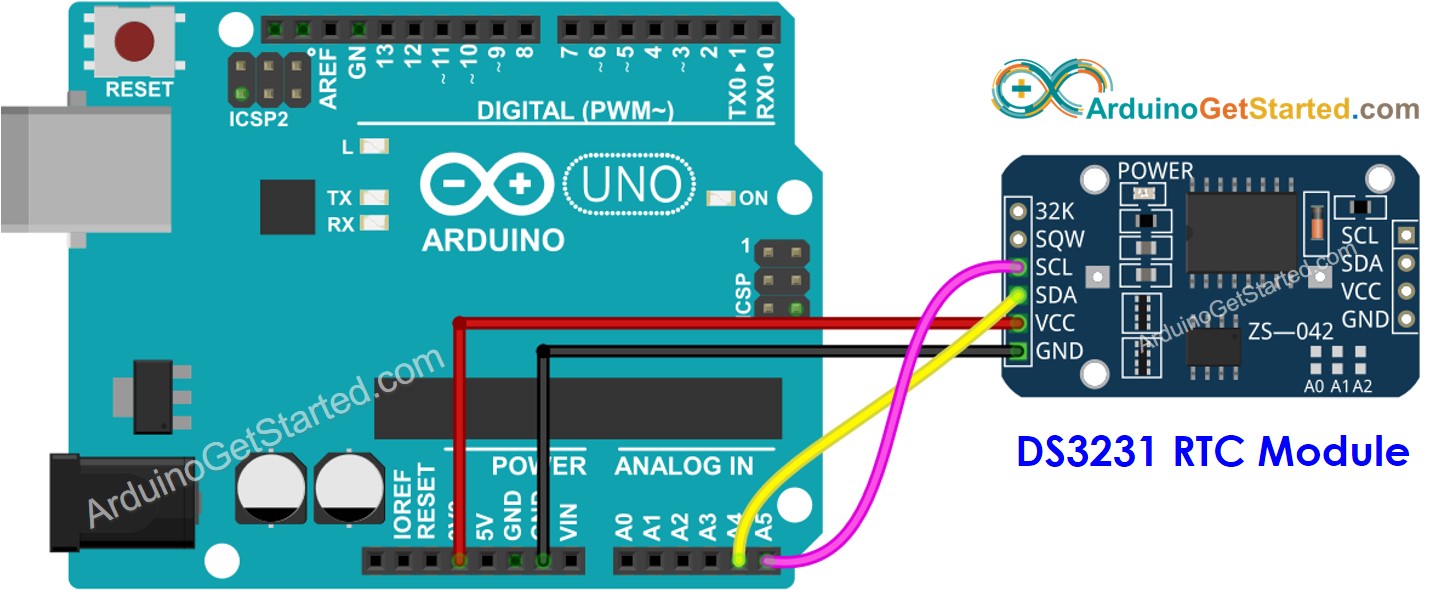
Cette image a été créée avec Fritzing. Cliquez pour agrandir l'image.
Arduino - Module RTC DS3231
| DS3231 RTC Module | Arduino Uno, Nano | Arduino Mega |
|---|---|---|
| Vin | 3.3V | 3.3V |
| GND | GND | GND |
| SDA | A4 | 20 |
| SCL | A5 | 21 |
Comment programmer le module RTC DS3231
- Inclure la bibliothèque :
- Déclarez un objet RTC :
- Initialiser le RTC :
- Pour la première fois, réglez la RTC à la date et à l'heure où le croquis a été compilé sur l'ordinateur.
- Lit les informations de date et d'heure à partir du module RTC
Code Arduino - Comment obtenir des données et l'heure
Étapes rapides
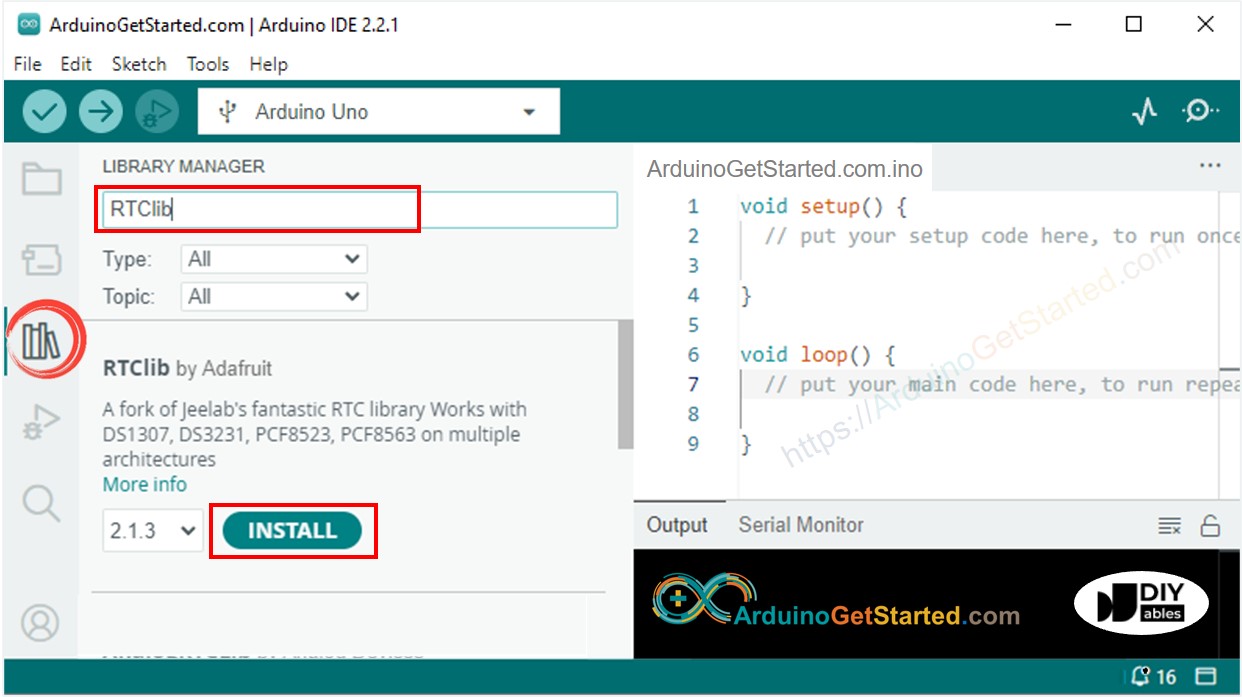
- Naviguez jusqu'à l'icône Libraries sur la barre gauche de l'IDE Arduino.
- Recherchez "RTClib", puis trouvez la bibliothèque RTC par Adafruit.
- Cliquez sur le bouton Install pour installer la bibliothèque RTC.
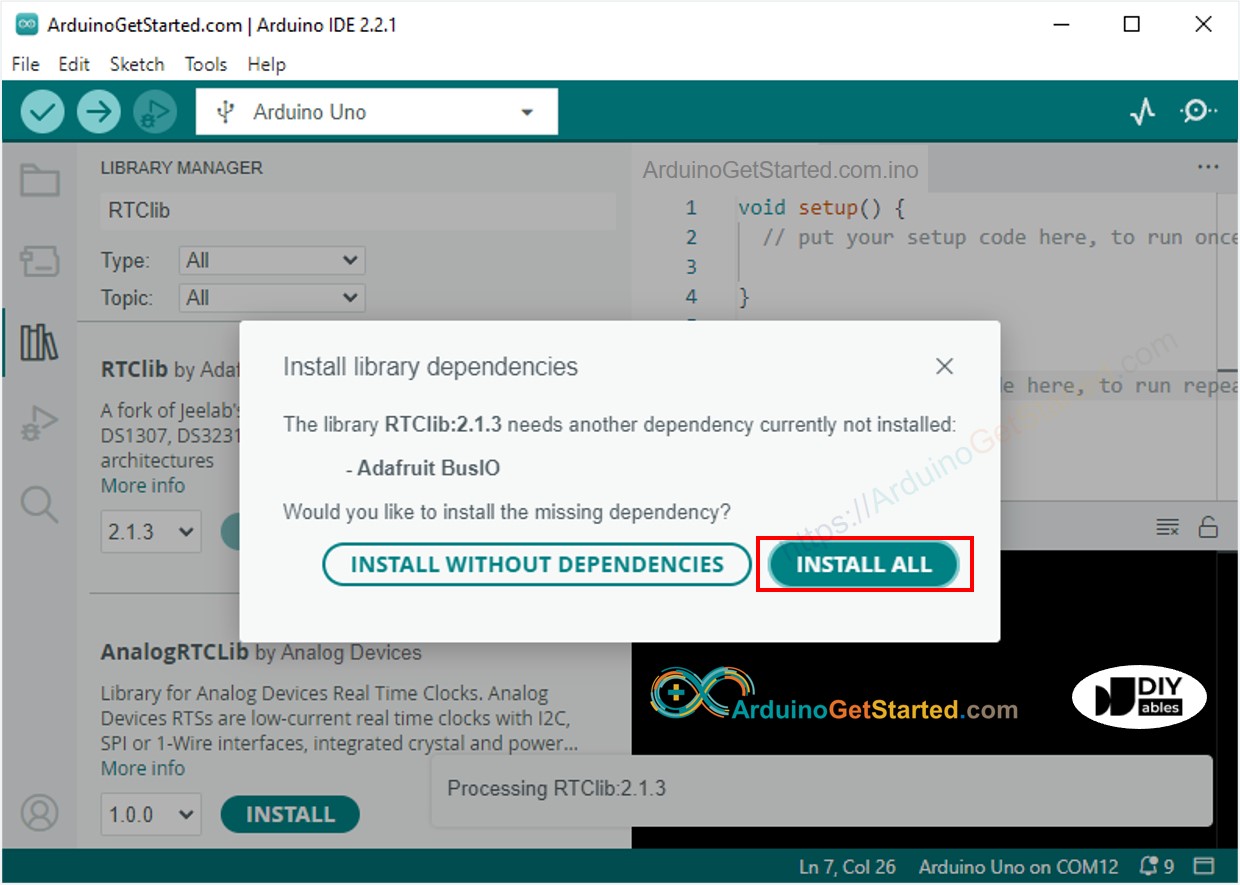
- Il se peut qu'on vous demande d'installer d'autres dépendances de bibliothèques.
- Cliquez sur le bouton Install All pour installer toutes les dépendances des bibliothèques.
- Copiez le code ci-dessus et ouvrez-le avec Arduino IDE
- Cliquez sur le bouton Upload dans l'Arduino IDE pour téléverser le code sur Arduino
- Ouvrez le moniteur série
- Voir le résultat sur le moniteur série.
