ESP32 - Feu de circulation
Dans ce tutoriel, nous explorerons comment utiliser l'ESP32 pour contrôler un module de feu de circulation. En détail, nous apprendrons :
- Comment connecter le module de feu de circulation à ESP32
- Comment programmer l'ESP32 pour contrôler un module de feu de circulation RGB
- Comment programmer l'ESP32 pour contrôler un module de feu de circulation RGB sans utiliser la fonction delay()
Préparation du matériel
Ou vous pouvez acheter les kits suivants:
| 1 | × | Kit de Démarrage DIYables ESP32 (ESP32 inclus) | |
| 1 | × | Kit de Capteurs DIYables (30 capteurs/écrans) | |
| 1 | × | Kit de Capteurs DIYables (18 capteurs/écrans) |
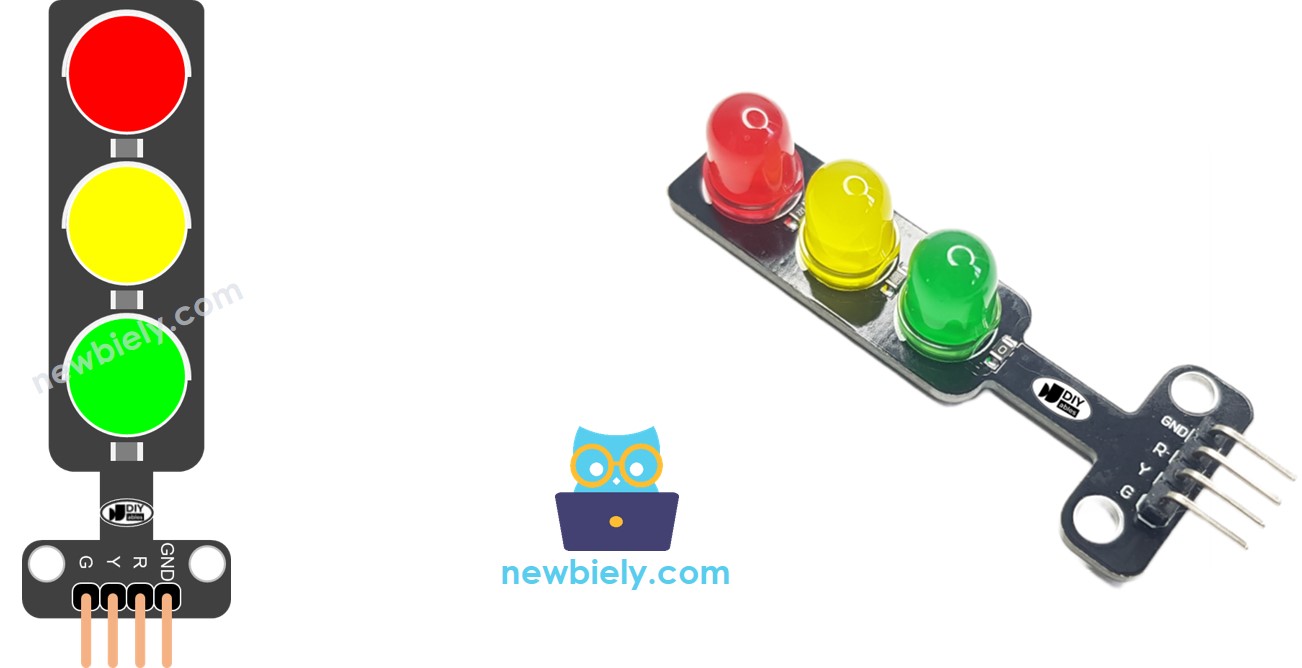
À propos du module de feux de circulation
Brochage
Un module de feu de circulation comprend 4 broches :
- Broche GND : La broche de masse, connectez cette broche au GND de l'ESP32.
- Broche R : La broche pour contrôler la lumière rouge, connectez cette broche à une sortie numérique de l'ESP32.
- Broche Y : La broche pour contrôler la lumière jaune, connectez cette broche à une sortie numérique de l'ESP32.
- Broche G : La broche pour contrôler la lumière verte, connectez cette broche à une sortie numérique de l'ESP32.

Comment ça marche
Diagramme de câblage
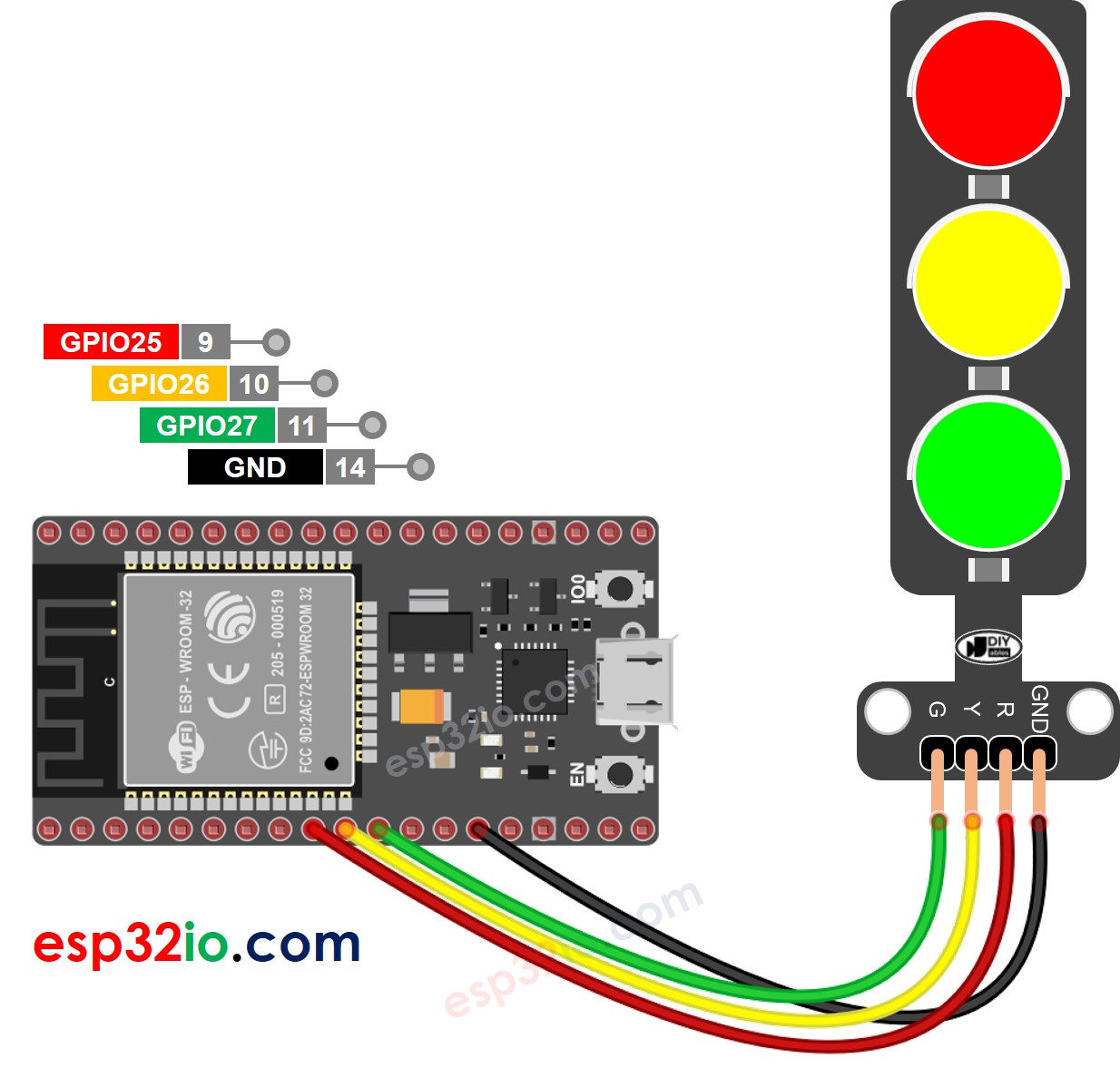
Cette image a été créée avec Fritzing. Cliquez pour agrandir l'image.
Si vous ne savez pas comment alimenter l'ESP32 et d'autres composants, consultez les instructions dans le tutoriel suivant : Comment alimenter l'ESP32..
- Avec une planche à pain
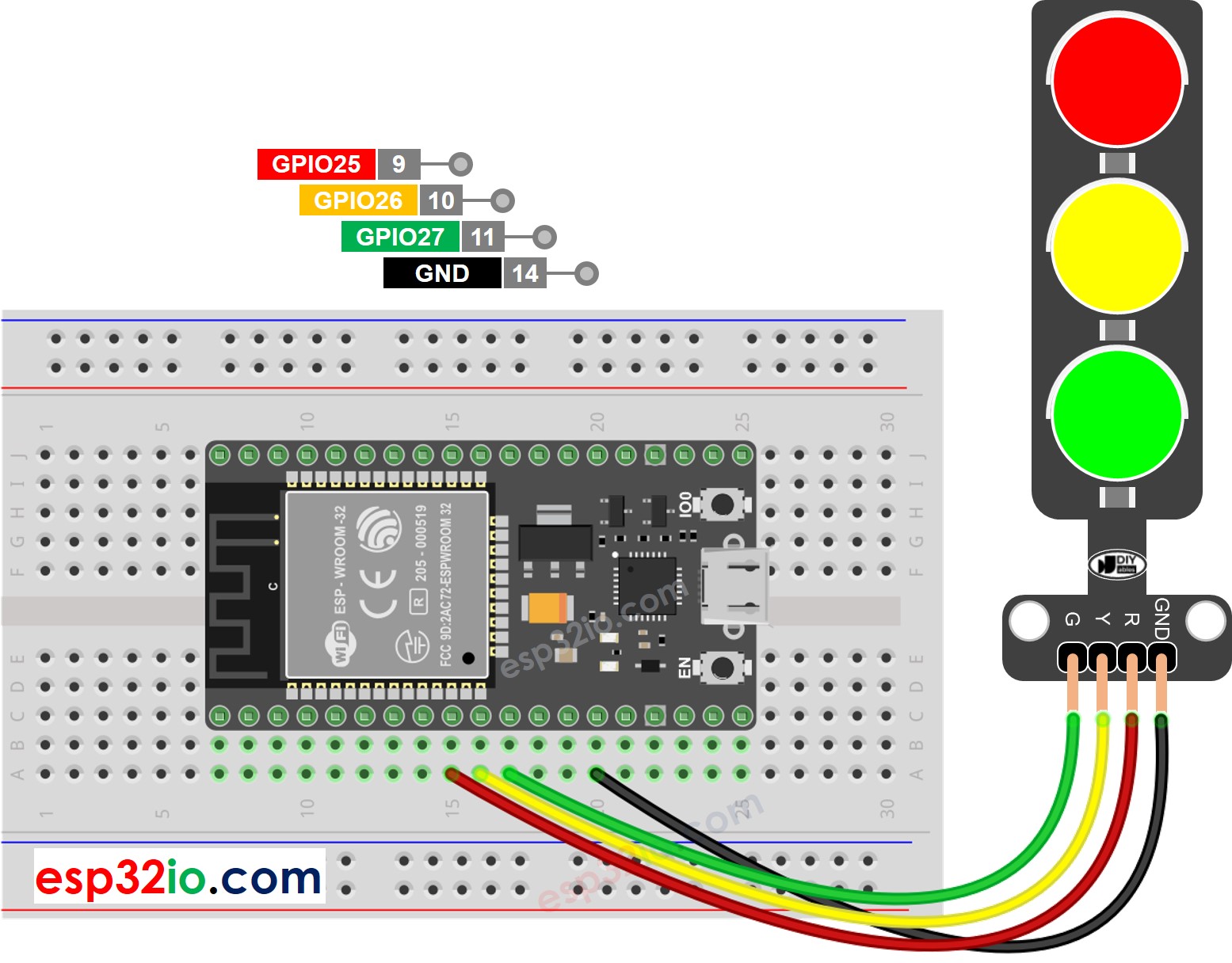
Cette image a été créée avec Fritzing. Cliquez pour agrandir l'image.
Comment programmer le module de feu de circulation
- Configurez les broches d'un ESP32 en mode de sortie numérique en utilisant la fonction pinMode().
- Programme pour activer la lumière rouge en utilisant la fonction digitalWrite() :
Code ESP32
Étapes rapides
- Si c'est la première fois que vous utilisez un ESP32, consultez Installation du logiciel ESP32..
- Effectuez le câblage comme sur l'image ci-dessus.
- Connectez la carte ESP32 à votre PC via un câble micro USB.
- Ouvrez Arduino IDE sur votre PC.
- Sélectionnez la bonne carte ESP32 (par exemple Module de développement ESP32) et le port COM.
- Copiez le code ci-dessus et ouvrez-le avec Arduino IDE.
- Cliquez sur le bouton Upload dans Arduino IDE pour charger le code sur ESP32.
- Vérifiez le module de feu de circulation.
Il est important de noter que le fonctionnement exact d'un feu de circulation peut varier selon la conception spécifique et la technologie utilisée dans différentes régions et intersections. Les principes décrits ci-dessus fournissent une compréhension générale de la manière dont les feux de circulation fonctionnent pour gérer le trafic et améliorer la sécurité sur les routes.
Le code ci-dessus démontre le contrôle individuel des lumières. Améliorons maintenant le code pour une meilleure optimisation.
Optimisation du code ESP32
- Améliorons le code en implémentant une fonction de contrôle de l'éclairage.
- Améliorons le code en utilisant une boucle for.
- Améliorons le code en utilisant la fonction millis() au lieu de delay().
