ESP32 - Ethernet
Ce didacticiel vous explique comment utiliser le module Ethernet W5500 pour connecter ESP32 à Internet ou à votre réseau LAN. En détail, nous apprendrons :
- Comment connecter ESP32 au module Ethernet W5500
- Comment programmer ESP32 pour faire une requête HTTP via Ethernet
- Comment programmer ESP32 pour créer un serveur web simple via Ethernet
Préparation du matériel
Ou vous pouvez acheter les kits suivants:
| 1 | × | Kit de Démarrage DIYables ESP32 (ESP32 inclus) | |
| 1 | × | Kit de Capteurs DIYables (30 capteurs/écrans) | |
| 1 | × | Kit de Capteurs DIYables (18 capteurs/écrans) |
À propos du module Ethernet W5500
Le module Ethernet W5500 possède deux interfaces :
- Interface RJ45 : pour se connecter au routeur/switch via un câble Ethernet
- Interface SPI : pour se connecter à la carte ESP32, comprenant 10 broches :
- Broche NC : laissez cette broche non connectée.
- Broche INT : laissez cette broche non connectée.
- Broche RST : broche de réinitialisation, connectez cette broche à la broche EN de l'ESP32.
- Broche GND : connectez cette broche à la broche GND de l'ESP32.
- Broche 5V : laissez cette broche non connectée.
- Broche 3.3V : connectez cette broche à la broche 3.3V de l'ESP32.
- Broche MISO : connectez cette broche à la broche SPI MISO de l'ESP32.
- Broche MOSI : connectez cette broche à la broche SPI MOSI de l'ESP32.
- Broche SCS : connectez cette broche à la broche SPI CS de l'ESP32.
- Broche SCLK : connectez cette broche à la broche SPI SCK de l'ESP32.
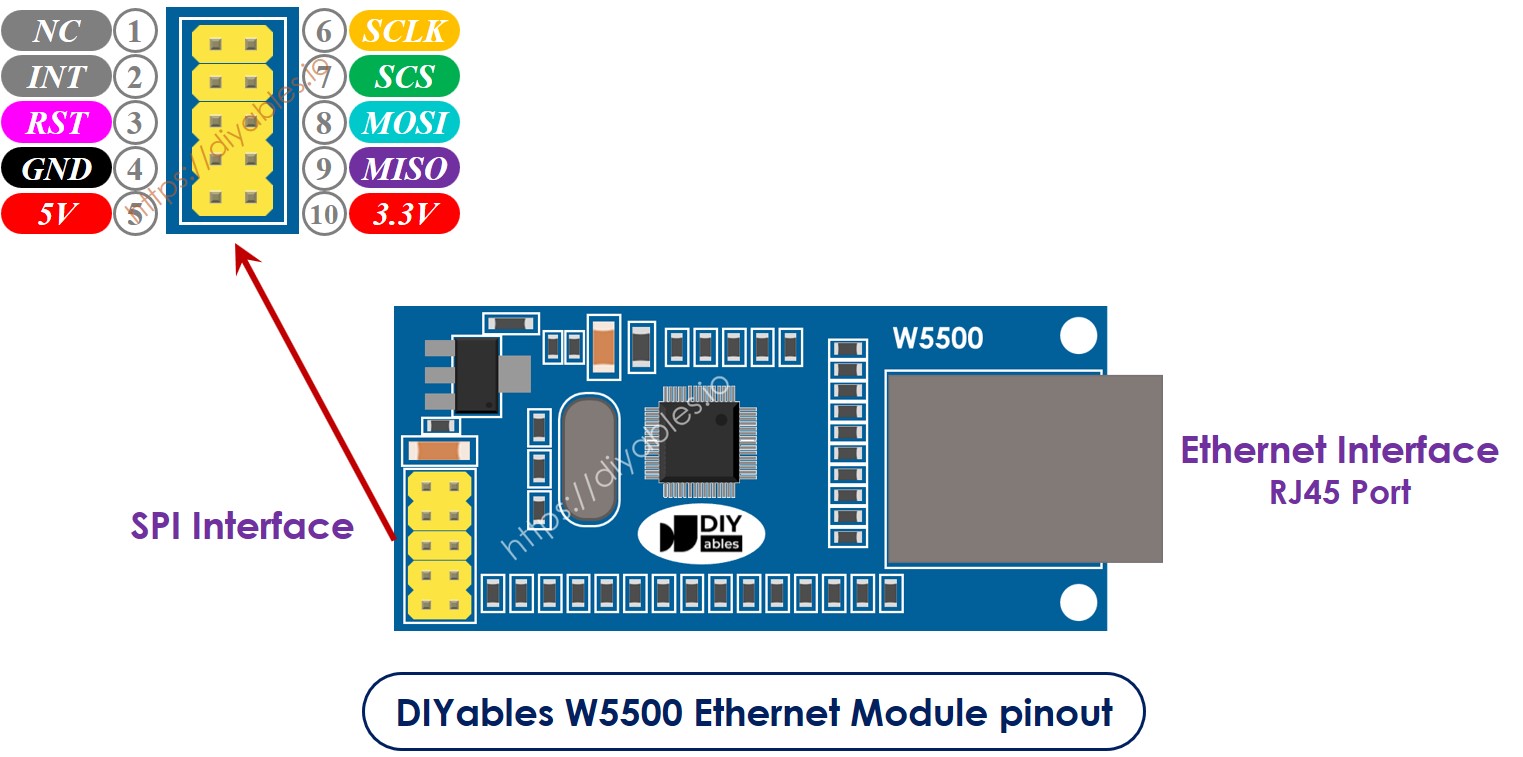
Schéma de câblage entre le module Ethernet ESP32 et W5500
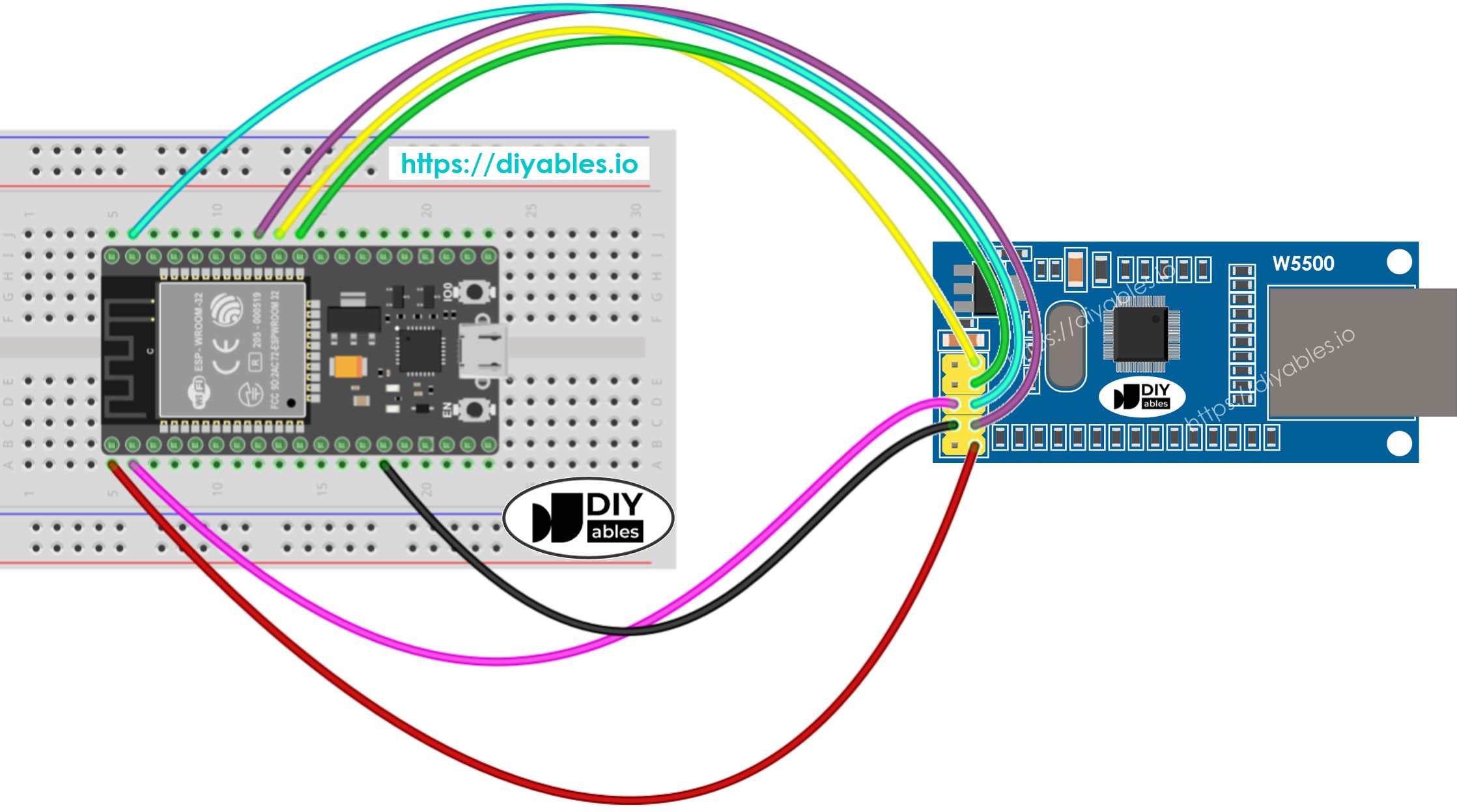
Cette image a été créée avec Fritzing. Cliquez pour agrandir l'image.
Si vous ne savez pas comment alimenter l'ESP32 et d'autres composants, consultez les instructions dans le tutoriel suivant : Comment alimenter l'ESP32..
Code ESP32 pour module Ethernet - Faire une requête HTTP via Ethernet
Le code suivant fonctionne comme un client web, effectuant des requêtes HTTP au serveur web à l'adresse http://example.com/.
Étapes rapides
- Si c'est la première fois que vous utilisez l'ESP32, consultez Installation du logiciel ESP32..
- Effectuez le câblage entre le module Ethernet et l'ESP32 comme indiqué dans le schéma de câblage ci-dessus
- Connectez l'ESP32 au PC via un câble USB
- Connectez le module Ethernet à votre routeur/switch via un câble Ethernet
- Ouvrez Arduino IDE sur votre PC.
- Sélectionnez la bonne carte ESP32 (par exemple, ESP32 Dev Module) et le bon port COM.
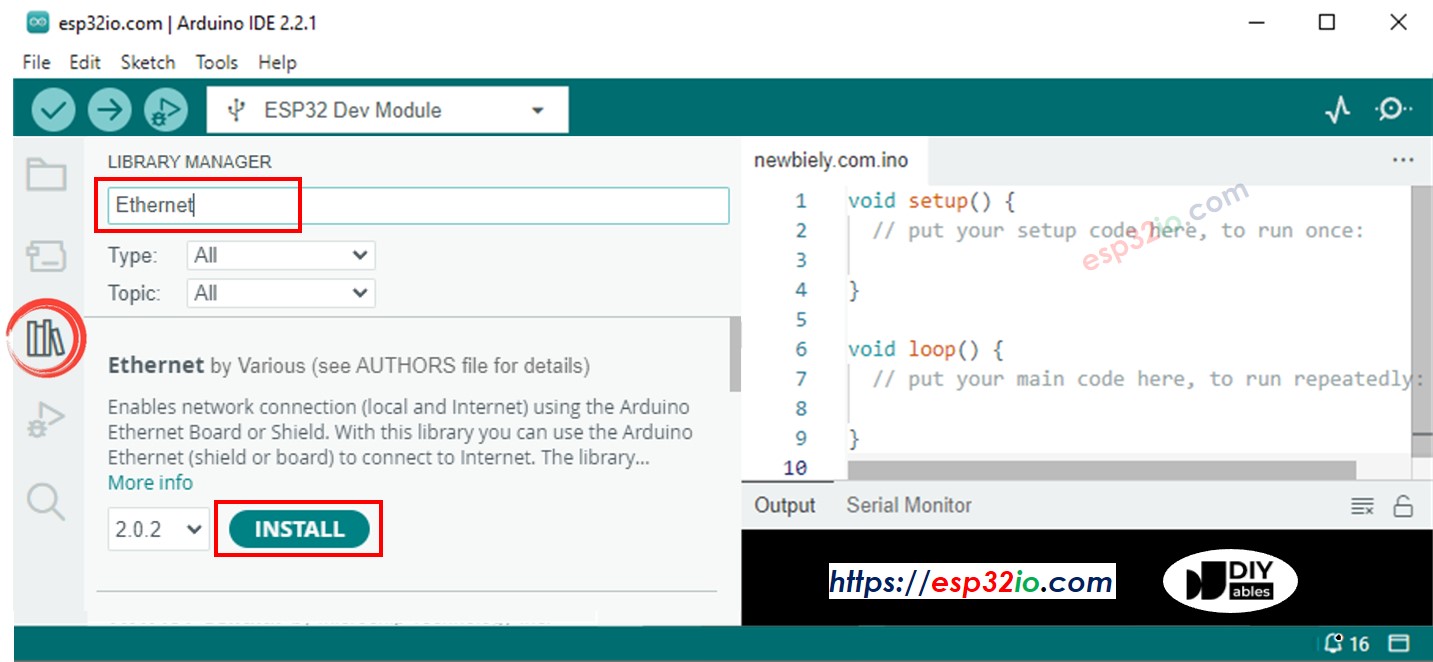
- Cliquez sur l'icône Libraries dans la barre de gauche de l'Arduino IDE.
- Recherchez “Ethernet”, puis trouvez la bibliothèque Ethernet par Various
- Cliquez sur le bouton Install pour installer la bibliothèque Ethernet.
- Ouvrir le Port Série dans Arduino IDE
- Copier le code ci-dessus et le coller dans Arduino IDE
- Cliquer sur le bouton Upload dans Arduino IDE pour télécharger le code vers l'ESP32
- Vérifier le résultat dans le Moniteur Série, cela ressemble à ce qui suit :
※ Note:
S'il y a un autre appareil sur le même réseau local avec la même adresse MAC, cela pourrait ne pas fonctionner.
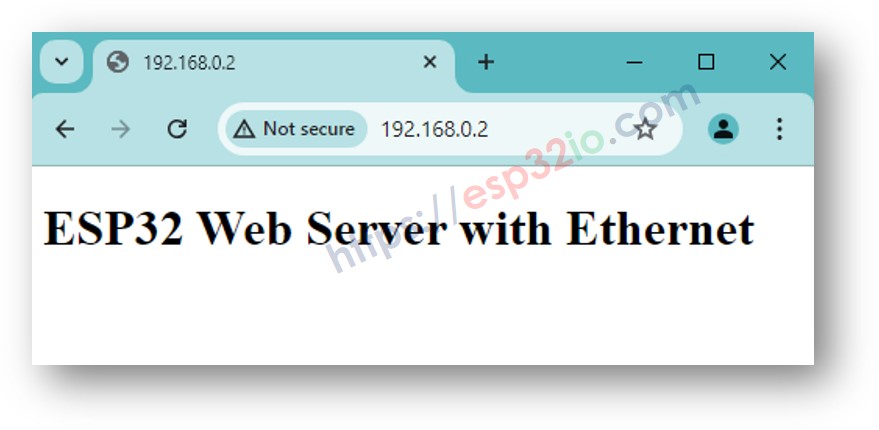
Code ESP32 pour module Ethernet - Serveur Web
Le code suivant transforme l'ESP32 en un serveur web qui répond aux navigateurs web avec une page web simple.
Étapes rapides
- Copiez le code ci-dessus et collez-le dans l'IDE Arduino
- Cliquez sur le bouton Upload dans l'IDE Arduino pour téléverser le code sur l'ESP32
- Consultez le résultat sur le Moniteur série, il ressemble à ceci :
- Copiez l'adresse IP ci-dessus et collez-la dans la barre d'adresse d'un navigateur web, vous verrez une page web simple servie par ESP32 comme suit :