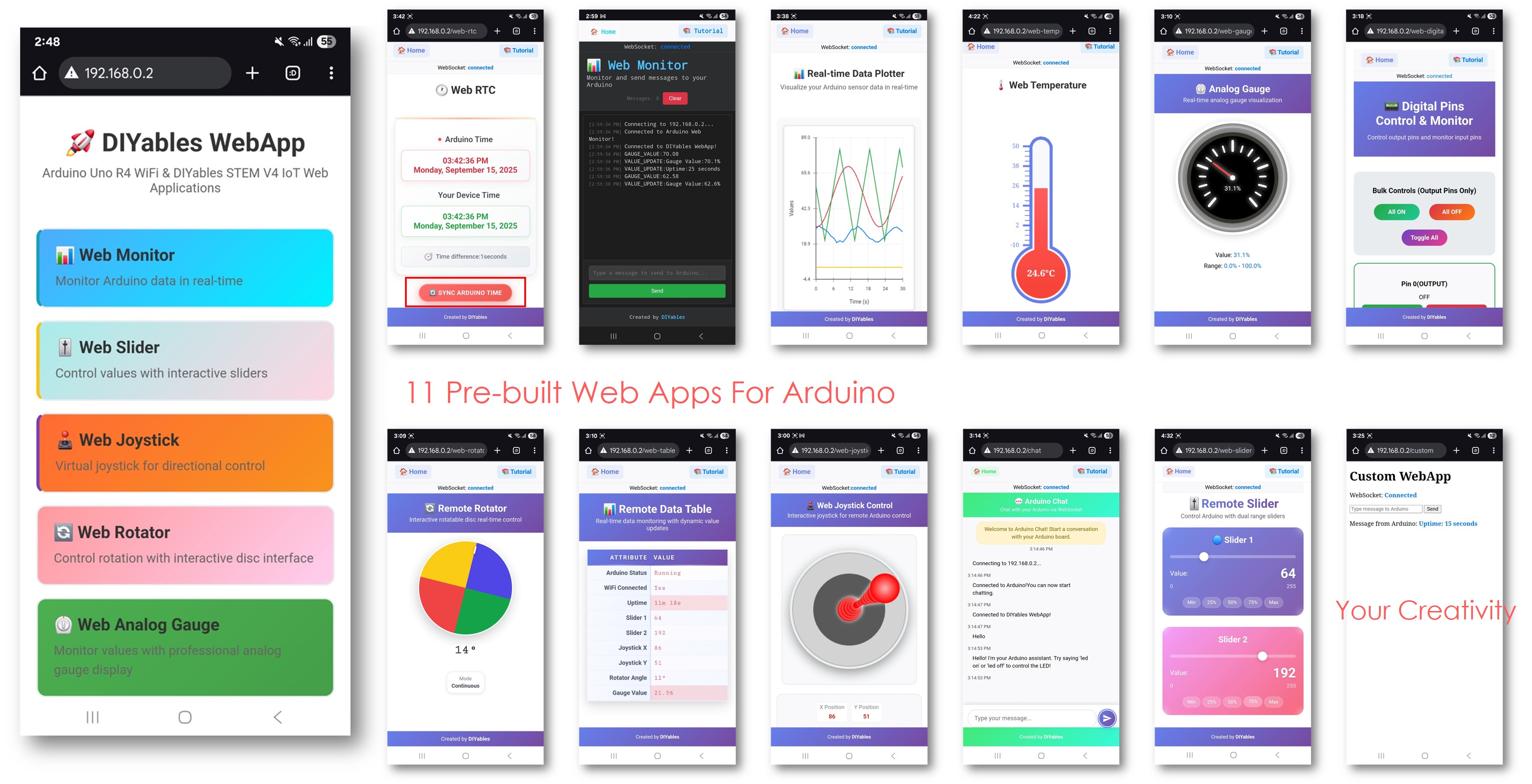
Cet exemple montre comment utiliser plusieurs applications web simultanément avec la bibliothèque WebApps de DIYables. Il illustre l'intégration de plusieurs interfaces web interactives — telles que la surveillance, le contrôle et la communication — au sein d'un seul projet. Conçu pour l'Arduino Uno R4 WiFi et la plateforme IoT STEM V4 de DIYables, cet exemple est idéal pour apprendre à combiner et à gérer plusieurs fonctionnalités basées sur le Web en même temps, fournissant une base solide pour des projets IoT avancés.
Suivez ces instructions étape par étape:
Connectez la carte Arduino Uno R4/DIYables STEM V4 IoT à votre ordinateur à l'aide d'un câble USB.
Ouvrez l'IDE Arduino sur votre ordinateur.
Sélectionnez la carte Arduino Uno R4 appropriée (par exemple, Arduino Uno R4 WiFi) et le port COM.
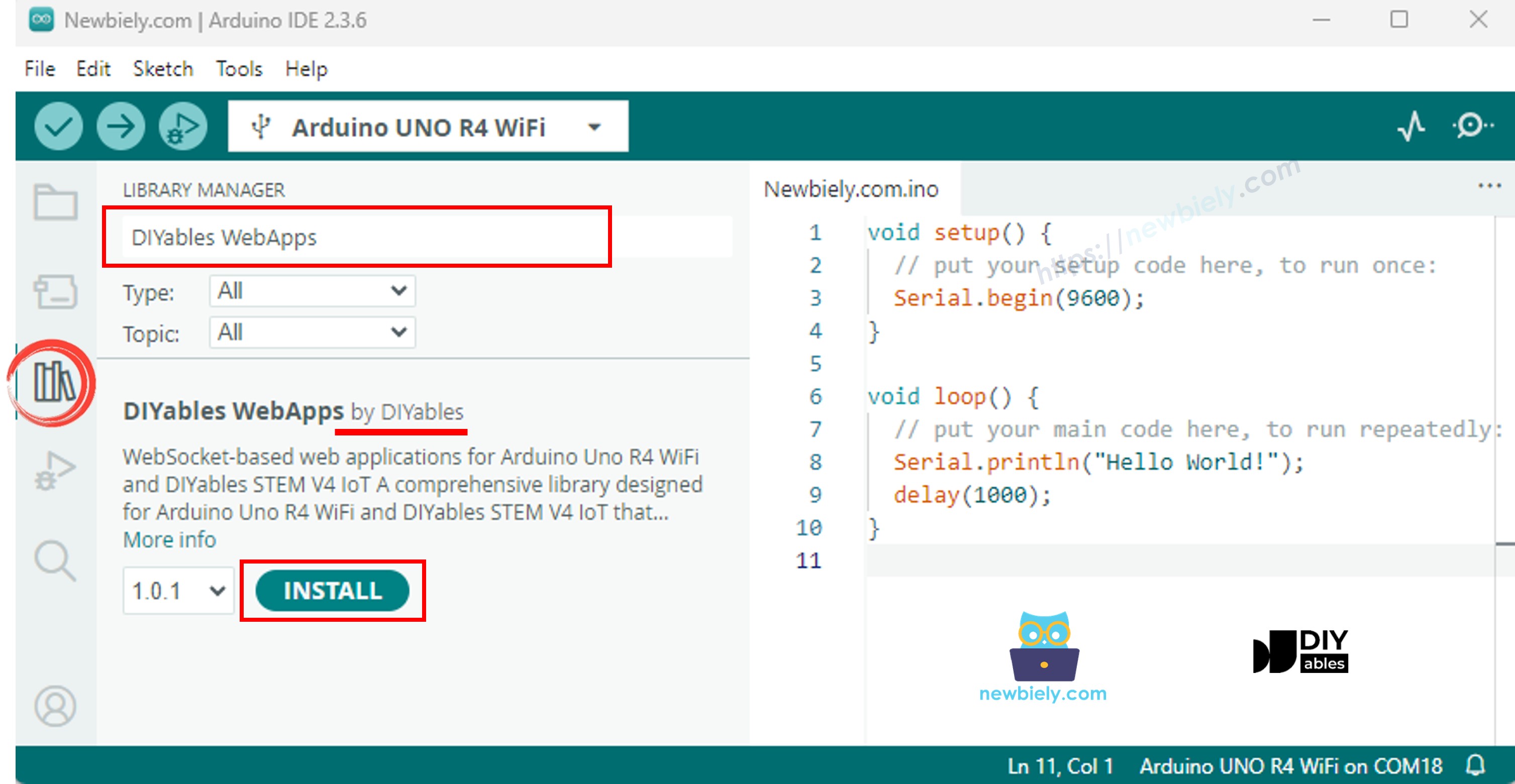
Accédez à l'icône Libraries dans la barre latérale gauche de l'IDE Arduino.
Recherchez "DIYables WebApps", puis trouvez la bibliothèque DIYables WebApps par DIYables.
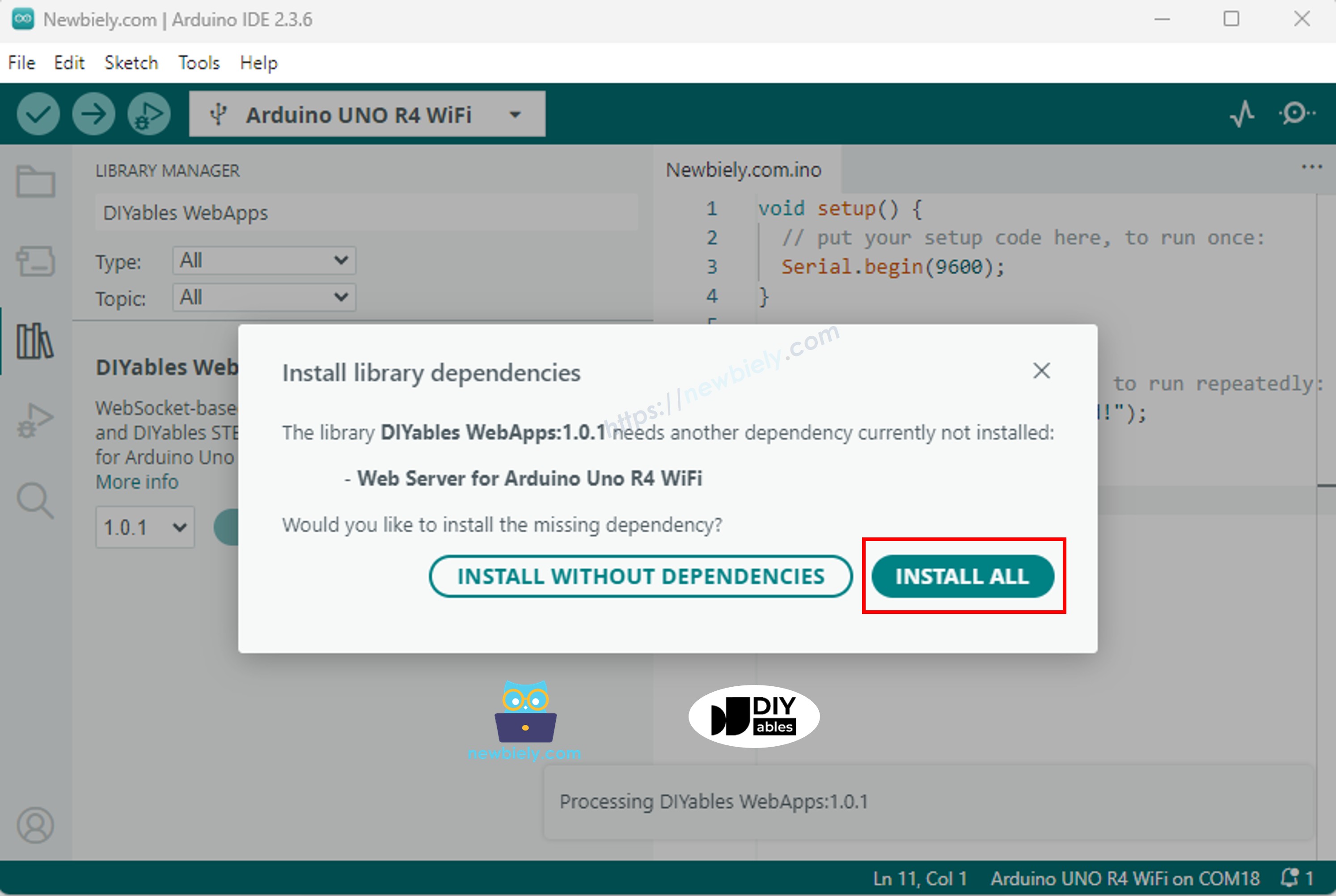
Cliquez sur le bouton Install pour installer la bibliothèque.
#include <DIYablesWebApps.h>
const char WIFI_SSID[] = "YOUR_WIFI_SSID";
const char WIFI_PASSWORD[] = "YOUR_WIFI_PASSWORD";
UnoR4ServerFactory factory;
DIYablesWebAppServer webAppsServer(factory, 80, 81);
DIYablesHomePage homePage;
DIYablesWebMonitorPage webMonitorPage;
DIYablesWebSliderPage webSliderPage;
DIYablesWebJoystickPage webJoystickPage(false, 5);
DIYablesWebRotatorPage webRotatorPage(ROTATOR_MODE_CONTINUOUS);
DIYablesWebAnalogGaugePage webAnalogGaugePage(0.0, 100.0, "%");
DIYablesWebTablePage webTablePage;
int currentSlider1 = 64;
int currentSlider2 = 128;
int currentJoystickX = 0;
int currentJoystickY = 0;
int currentRotatorAngle = 0;
float currentGaugeValue = 50.0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
delay(1000);
Serial.println("DIYables WebApp - Multiple Apps Example");
webAppsServer.addApp(&homePage);
webAppsServer.addApp(&webMonitorPage);
webAppsServer.addApp(&webSliderPage);
webAppsServer.addApp(&webJoystickPage);
webAppsServer.addApp(&webRotatorPage);
webAppsServer.addApp(&webAnalogGaugePage);
webAppsServer.addApp(&webTablePage);
webAppsServer.setNotFoundPage(DIYablesNotFoundPage());
webTablePage.addRow("Arduino Status");
webTablePage.addRow("WiFi Connected");
webTablePage.addRow("Uptime");
webTablePage.addRow("Slider 1");
webTablePage.addRow("Slider 2");
webTablePage.addRow("Joystick X");
webTablePage.addRow("Joystick Y");
webTablePage.addRow("Rotator Angle");
webTablePage.addRow("Gauge Value");
if (!webAppsServer.begin(WIFI_SSID, WIFI_PASSWORD)) {
while (1) {
Serial.println("Failed to start WebApp server!");
delay(1000);
}
}
setupCallbacks();
}
void setupCallbacks() {
webMonitorPage.onWebMonitorMessage([](const String& message) {
Serial.println("Web Monitor: " + message);
webMonitorPage.sendToWebMonitor("Arduino received: " + message);
});
webSliderPage.onSliderValueFromWeb([](int slider1, int slider2) {
currentSlider1 = slider1;
currentSlider2 = slider2;
Serial.print("Slider 1: ");
Serial.print(slider1);
Serial.print(", Slider 2: ");
Serial.println(slider2);
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Slider 1", String(slider1));
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Slider 2", String(slider2));
currentGaugeValue = map(slider1, 0, 255, 0, 100);
webAnalogGaugePage.sendToWebAnalogGauge(currentGaugeValue);
char gaugeStr[16];
snprintf(gaugeStr, sizeof(gaugeStr), "%.1f%%", currentGaugeValue);
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Gauge Value", String(gaugeStr));
});
webSliderPage.onSliderValueToWeb([]() {
webSliderPage.sendToWebSlider(currentSlider1, currentSlider2);
});
webJoystickPage.onJoystickValueFromWeb([](int x, int y) {
currentJoystickX = x;
currentJoystickY = y;
Serial.print("Joystick - X: ");
Serial.print(x);
Serial.print(", Y: ");
Serial.println(y);
Serial.print(x);
Serial.print(", Y: ");
Serial.println(y);
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Joystick X", String(x));
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Joystick Y", String(y));
}
});
webJoystickPage.onJoystickValueToWeb([]() {
webJoystickPage.sendToWebJoystick(currentJoystickX, currentJoystickY);
});
webRotatorPage.onRotatorAngleFromWeb([](float angle) {
currentRotatorAngle = (int)angle;
Serial.println("Rotator angle: " + String(angle) + "°");
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Rotator Angle", String(angle, 0) + "°");
});
webAnalogGaugePage.onGaugeValueRequest([]() {
webAnalogGaugePage.sendToWebAnalogGauge(currentGaugeValue);
});
webTablePage.onTableValueRequest([]() {
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Arduino Status", "Running");
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("WiFi Connected", "Yes");
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Uptime", "0 seconds");
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Slider 1", String(currentSlider1));
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Slider 2", String(currentSlider2));
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Joystick X", String(currentJoystickX));
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Joystick Y", String(currentJoystickY));
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Rotator Angle", String(currentRotatorAngle) + "°");
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Gauge Value", String(currentGaugeValue, 1) + "%");
});
}
void loop() {
webAppsServer.loop();
static unsigned long lastUptimeUpdate = 0;
if (millis() - lastUptimeUpdate > 5000) {
lastUptimeUpdate = millis();
unsigned long uptimeSeconds = millis() / 1000;
String uptimeStr = String(uptimeSeconds) + " seconds";
if (uptimeSeconds >= 60) {
uptimeStr = String(uptimeSeconds / 60) + "m " + String(uptimeSeconds % 60) + "s";
}
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Uptime", uptimeStr);
}
static unsigned long lastSensorUpdate = 0;
if (millis() - lastSensorUpdate > 3000) {
lastSensorUpdate = millis();
float sensorValue = 50.0 + 30.0 * sin(millis() / 10000.0);
currentGaugeValue = sensorValue;
webAnalogGaugePage.sendToWebAnalogGauge(currentGaugeValue);
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Gauge Value", String(currentGaugeValue, 1) + "%");
}
delay(10);
}
const char WIFI_SSID[] = "YOUR_WIFI_NETWORK";
const char WIFI_PASSWORD[] = "YOUR_WIFI_PASSWORD";
DIYables WebApp - Multiple Apps Example
INFO: Added app /
INFO: Added app /web-monitor
INFO: Added app /web-slider
INFO: Added app /web-joystick
INFO: Added app /web-rotator
INFO: Added app /web-gauge
INFO: Added app /web-table
DIYables WebApp Library
Platform: Arduino Uno R4 WiFi
Network connected!
IP address: 192.168.0.2
HTTP server started on port 80
Configuring WebSocket server callbacks...
WebSocket server started on port 81
WebSocket URL: ws://192.168.0.2:81
WebSocket server started on port 81
==========================================
DIYables WebApp Ready!
==========================================
📱 Web Interface: http://192.168.0.2
🔗 WebSocket: ws://192.168.0.2:81
📋 Available Applications:
🏠 Home Page: http://192.168.0.2/
📊 Web Monitor: http://192.168.0.2/web-monitor
🎚️ Web Slider: http://192.168.0.2/web-slider
🕹️ Web Joystick: http://192.168.0.2/web-joystick
🔄 Web Rotator: http://192.168.0.2/web-rotator
⏲️ Web Analog Gauge: http://192.168.0.2/web-gauge
📊 Web Table: http://192.168.0.2/web-table
==========================================
Si vous ne voyez rien, redémarrez la carte Arduino.
Prenez note de l'adresse IP affichée et saisissez cette adresse dans la barre d'adresse d'un navigateur web sur votre smartphone ou sur votre PC.
Exemple : http://192.168.0.2
Vous verrez la page d'accueil avec toutes les applications web comme sur l'image ci-dessous.
Cliquez sur n'importe quel lien d'une application web (Chat, Web Monitor, Web Digital Pins, Web Slider, Web Joystick, etc.), vous verrez l'interface utilisateur de l'application web correspondante.
Ou vous pouvez également accéder directement à chaque page en utilisant l'adresse IP suivie du chemin de l'application. Par exemple : http://192.168.0.2/chat, http://192.168.0.2/web-monitor, etc.
Explorez toutes les applications web : essayez de discuter avec Arduino, surveillez la sortie série, contrôlez les broches numériques, ajustez les curseurs et utilisez le joystick virtuel pour découvrir toutes les capacités de l'interface web intégrée.
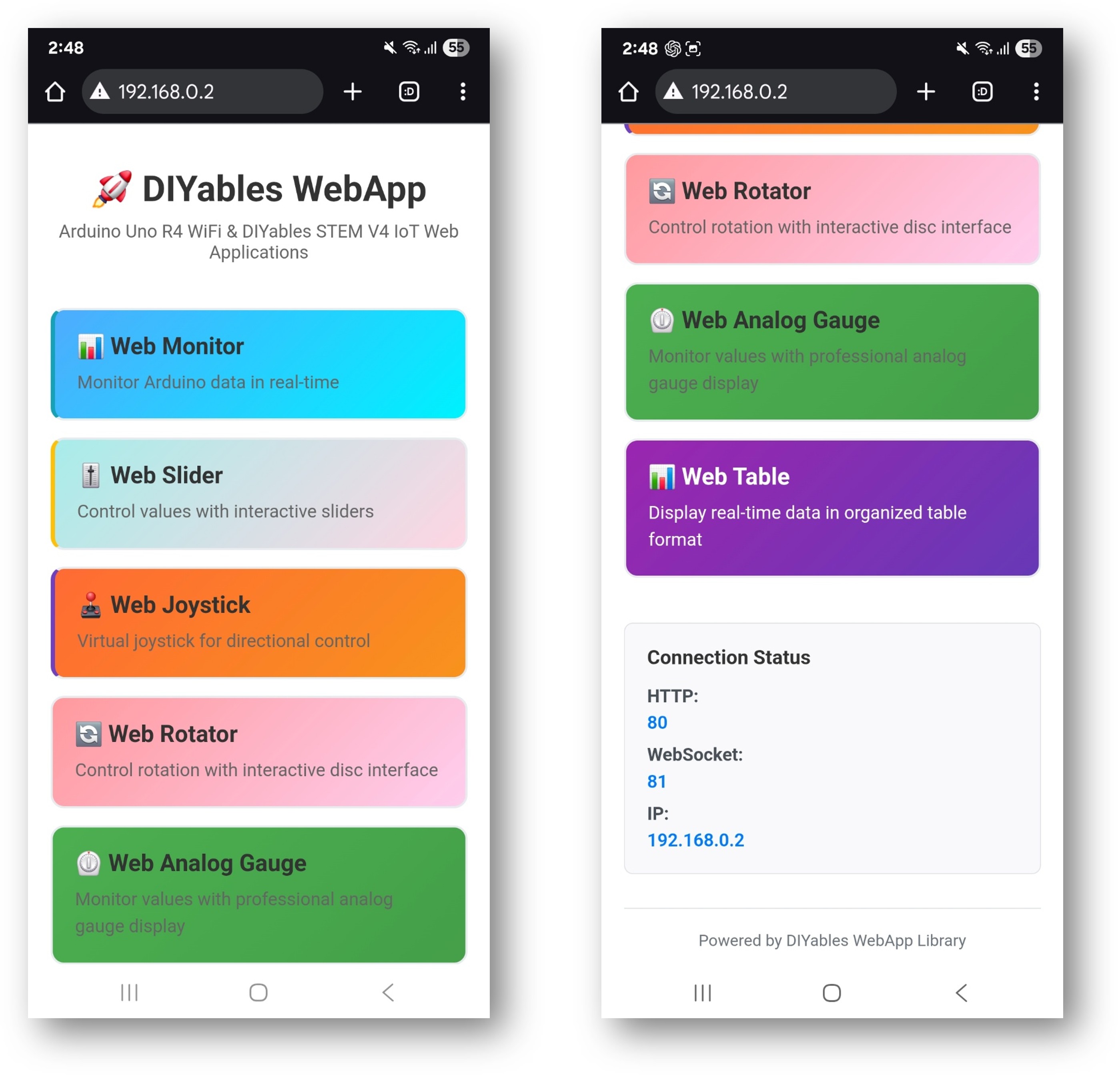
La page d'accueil sert de centre de contrôle avec des liens vers toutes les applications :
Moniteur Web: /webmonitor - Interface de communication série
Chat: /chat - Messagerie interactive avec Arduino
Broches numériques: /digital-pins - Contrôle et surveillance des broches
Curseur Web: /webslider - Deux curseurs de contrôle analogiques
Joystick Web: /webjoystick - Interface de contrôle de position en 2D
Accédez directement à chaque interface :
http://[ARDUINO_IP]/ # Home page
http://[ARDUINO_IP]/webmonitor # Serial monitor interface
http://[ARDUINO_IP]/chat # Chat interface
http://[ARDUINO_IP]/digital-pins # Pin control
http://[ARDUINO_IP]/webslider # Slider controls
http://[ARDUINO_IP]/webjoystick # Joystick control
Cet exemple exhaustif offre une base pour vos projets créatifs. Modifiez et adaptez les configurations ci-dessous pour créer des applications IoT incroyables qui correspondent à votre vision unique.
L'exemple préconfigure des broches spécifiques pour différentes utilisations :
webDigitalPinsPage.enablePin(2, WEB_PIN_OUTPUT);
webDigitalPinsPage.enablePin(3, WEB_PIN_OUTPUT);
webDigitalPinsPage.enablePin(4, WEB_PIN_OUTPUT);
webDigitalPinsPage.enablePin(13, WEB_PIN_OUTPUT);
webDigitalPinsPage.enablePin(8, WEB_PIN_INPUT);
webDigitalPinsPage.enablePin(9, WEB_PIN_INPUT);
DIYablesWebJoystickPage webJoystickPage(false, 5);
L'exemple maintient un état synchronisé à travers toutes les interfaces :
int pinStates[16] = { LOW };
int currentSlider1 = 64;
int currentSlider2 = 128;
int currentJoystickX = 0;
int currentJoystickY = 0;
L'interface de chat comprend plusieurs commandes préprogrammées :
hello - Réponse de salutation amicale
time - Affiche le temps de fonctionnement d'Arduino en secondes
status - Rapporte l'état d'Arduino et l'état de la LED
help - Liste les commandes disponibles
User: hello
Arduino: Hello! I'm your Arduino. How can I help you?
User: led on
Arduino: Built-in LED is now ON!
User: time
Arduino: I've been running for 1245 seconds.
User: status
Arduino: Status: Running smoothly! LED is ON
#include <Servo.h>
const int MOTOR_LEFT_PWM = 9;
const int MOTOR_RIGHT_PWM = 10;
const int SERVO_PAN = 11;
const int SERVO_TILT = 12;
const int LED_STRIP_PIN = 6;
Servo panServo, tiltServo;
void setup() {
panServo.attach(SERVO_PAN);
tiltServo.attach(SERVO_TILT);
pinMode(MOTOR_LEFT_PWM, OUTPUT);
pinMode(MOTOR_RIGHT_PWM, OUTPUT);
setupRobotCallbacks();
}
void setupRobotCallbacks() {
webJoystickPage.onJoystickValueFromWeb([](int x, int y) {
int leftSpeed = y + (x / 2);
int rightSpeed = y - (x / 2);
leftSpeed = constrain(leftSpeed, -100, 100);
rightSpeed = constrain(rightSpeed, -100, 100);
leftSpeed = map(leftSpeed, -100, 100, -currentSlider1, currentSlider1);
rightSpeed = map(rightSpeed, -100, 100, -currentSlider1, currentSlider1);
analogWrite(MOTOR_LEFT_PWM, abs(leftSpeed));
analogWrite(MOTOR_RIGHT_PWM, abs(rightSpeed));
Serial.println("Robot - Left: " + String(leftSpeed) + ", Right: " + String(rightSpeed));
});
webSliderPage.onSliderValueFromWeb([](int slider1, int slider2) {
int panAngle = map(currentJoystickX, -100, 100, 0, 180);
int tiltAngle = map(slider2, 0, 255, 0, 180);
panServo.write(panAngle);
tiltServo.write(tiltAngle);
Serial.println("Camera - Pan: " + String(panAngle) + "°, Tilt: " + String(tiltAngle) + "°");
});
webDigitalPinsPage.onPinWrite([](int pin, int state) {
switch (pin) {
case 2:
digitalWrite(pin, state);
Serial.println("Headlights " + String(state ? "ON" : "OFF"));
break;
case 3:
if (state) {
digitalWrite(pin, HIGH);
delay(200);
digitalWrite(pin, LOW);
}
break;
case 4:
if (state) {
analogWrite(MOTOR_LEFT_PWM, 0);
analogWrite(MOTOR_RIGHT_PWM, 0);
Serial.println("EMERGENCY STOP ACTIVATED");
}
break;
}
});
chatPage.onChatMessage([](const String& message) {
String msg = message;
msg.toLowerCase();
if (msg.indexOf("stop") >= 0) {
analogWrite(MOTOR_LEFT_PWM, 0);
analogWrite(MOTOR_RIGHT_PWM, 0);
chatPage.sendToChat("Robot stopped!");
return;
}
if (msg.indexOf("center camera") >= 0) {
panServo.write(90);
tiltServo.write(90);
chatPage.sendToChat("Camera centered!");
return;
}
if (msg.indexOf("speed") >= 0) {
String response = "Current max speed: " + String(map(currentSlider1, 0, 255, 0, 100)) + "%";
chatPage.sendToChat(response);
return;
}
chatPage.sendToChat("Robot commands: stop, center camera, speed");
});
}
const int LIVING_ROOM_LIGHTS = 2;
const int BEDROOM_LIGHTS = 3;
const int KITCHEN_LIGHTS = 4;
const int FAN_CONTROL = 9;
const int AC_CONTROL = 10;
const int MOTION_SENSOR = 8;
const int DOOR_SENSOR = 9;
void setupHomeAutomation() {
pinMode(LIVING_ROOM_LIGHTS, OUTPUT);
pinMode(BEDROOM_LIGHTS, OUTPUT);
pinMode(KITCHEN_LIGHTS, OUTPUT);
pinMode(FAN_CONTROL, OUTPUT);
pinMode(AC_CONTROL, OUTPUT);
pinMode(MOTION_SENSOR, INPUT);
pinMode(DOOR_SENSOR, INPUT_PULLUP);
webDigitalPinsPage.onPinWrite([](int pin, int state) {
digitalWrite(pin, state);
String room;
switch (pin) {
case 2: room = "Living Room"; break;
case 3: room = "Bedroom"; break;
case 4: room = "Kitchen"; break;
default: room = "Pin " + String(pin); break;
}
Serial.println(room + " lights " + String(state ? "ON" : "OFF"));
String message = room + " lights turned " + String(state ? "ON" : "OFF");
chatPage.sendToChat(message);
});
webSliderPage.onSliderValueFromWeb([](int slider1, int slider2) {
analogWrite(FAN_CONTROL, slider1);
analogWrite(AC_CONTROL, slider2);
Serial.println("Fan: " + String(map(slider1, 0, 255, 0, 100)) + "%, " +
"AC: " + String(map(slider2, 0, 255, 0, 100)) + "%");
});
chatPage.onChatMessage([](const String& message) {
String msg = message;
msg.toLowerCase();
if (msg.indexOf("all lights on") >= 0) {
digitalWrite(LIVING_ROOM_LIGHTS, HIGH);
digitalWrite(BEDROOM_LIGHTS, HIGH);
digitalWrite(KITCHEN_LIGHTS, HIGH);
chatPage.sendToChat("All lights turned ON!");
return;
}
if (msg.indexOf("all lights off") >= 0) {
digitalWrite(LIVING_ROOM_LIGHTS, LOW);
digitalWrite(BEDROOM_LIGHTS, LOW);
digitalWrite(KITCHEN_LIGHTS, LOW);
chatPage.sendToChat("All lights turned OFF!");
return;
}
if (msg.indexOf("temperature") >= 0) {
String response = "Fan: " + String(map(currentSlider1, 0, 255, 0, 100)) + "%, " +
"AC: " + String(map(currentSlider2, 0, 255, 0, 100)) + "%";
chatPage.sendToChat(response);
return;
}
if (msg.indexOf("security") >= 0) {
bool motion = digitalRead(MOTION_SENSOR);
bool door = digitalRead(DOOR_SENSOR);
String status = "Motion: " + String(motion ? "DETECTED" : "CLEAR") +
", Door: " + String(door ? "CLOSED" : "OPEN");
chatPage.sendToChat(status);
return;
}
chatPage.sendToChat("Home commands: all lights on/off, temperature, security");
});
}
void loop() {
server.loop();
static bool lastMotion = false;
static bool lastDoor = false;
bool currentMotion = digitalRead(MOTION_SENSOR);
bool currentDoor = digitalRead(DOOR_SENSOR);
if (currentMotion != lastMotion) {
if (currentMotion) {
chatPage.sendToChat("🚨 MOTION DETECTED!");
webMonitorPage.sendToWebMonitor("Security Alert: Motion detected");
}
lastMotion = currentMotion;
}
if (currentDoor != lastDoor) {
String status = currentDoor ? "CLOSED" : "OPENED";
chatPage.sendToChat("🚪 Door " + status);
webMonitorPage.sendToWebMonitor("Security: Door " + status);
lastDoor = currentDoor;
}
delay(10);
}
const int HEATING_ELEMENT = 9;
const int COOLING_FAN = 10;
const int STIRRER_MOTOR = 11;
const int TEMP_SENSOR_PIN = A0;
const int PH_SENSOR_PIN = A1;
void setupScienceExperiment() {
webSliderPage.onSliderValueFromWeb([](int slider1, int slider2) {
int targetTemp = map(slider1, 0, 255, 20, 80);
analogWrite(STIRRER_MOTOR, slider2);
int currentTemp = readTemperature();
if (currentTemp < targetTemp) {
analogWrite(HEATING_ELEMENT, 200);
analogWrite(COOLING_FAN, 0);
} else if (currentTemp > targetTemp + 2) {
analogWrite(HEATING_ELEMENT, 0);
analogWrite(COOLING_FAN, 255);
} else {
analogWrite(HEATING_ELEMENT, 0);
analogWrite(COOLING_FAN, 0);
}
Serial.println("Target: " + String(targetTemp) + "°C, Current: " + String(currentTemp) + "°C");
});
chatPage.onChatMessage([](const String& message) {
String msg = message;
msg.toLowerCase();
if (msg.indexOf("data") >= 0) {
int temp = readTemperature();
float ph = readPH();
String data = "Temperature: " + String(temp) + "°C, pH: " + String(ph, 2);
chatPage.sendToChat(data);
return;
}
if (msg.indexOf("start") >= 0) {
chatPage.sendToChat("🔬 Experiment started! Monitoring conditions...");
return;
}
if (msg.indexOf("stop") >= 0) {
analogWrite(HEATING_ELEMENT, 0);
analogWrite(COOLING_FAN, 0);
analogWrite(STIRRER_MOTOR, 0);
chatPage.sendToChat("⚠️ Experiment stopped - all systems OFF");
return;
}
chatPage.sendToChat("Science commands: data, start, stop");
});
webMonitorPage.onWebMonitorMessage([](const String& message) {
if (message == "log") {
int temp = readTemperature();
float ph = readPH();
String logEntry = String(millis()) + "," + String(temp) + "," + String(ph, 2);
webMonitorPage.sendToWebMonitor(logEntry);
}
});
}
int readTemperature() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(TEMP_SENSOR_PIN);
return map(sensorValue, 0, 1023, 0, 100);
}
float readPH() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(PH_SENSOR_PIN);
return map(sensorValue, 0, 1023, 0, 14) / 10.0;
}
void synchronizeAllStates() {
webSliderPage.sendToWebSlider(currentSlider1, currentSlider2);
webJoystickPage.sendToWebJoystick(currentJoystickX, currentJoystickY);
for (int pin = 0; pin <= 13; pin++) {
if (webDigitalPinsPage.isPinEnabled(pin)) {
webDigitalPinsPage.updatePinState(pin, pinStates[pin]);
}
}
Serial.println("All interface states synchronized");
}
void setupCrossInterfaceCommunication() {
webJoystickPage.onJoystickValueFromWeb([](int x, int y) {
float distance = sqrt(x*x + y*y);
if (distance > 50) {
int maxValue = map(distance, 50, 100, 255, 128);
}
});
webDigitalPinsPage.onPinWrite([](int pin, int state) {
if (pin == 2 && state == HIGH) {
chatPage.sendToChat("📢 System armed - additional commands available");
} else if (pin == 2 && state == LOW) {
chatPage.sendToChat("📢 System disarmed - limited commands only");
}
});
}
1. Certaines interfaces ne se chargent pas
Vérifiez que toutes les applications sont ajoutées au serveur dans setup()
Vérifiez les connexions WebSocket dans la console du navigateur
Assurez-vous d'avoir suffisamment de mémoire pour toutes les interfaces
2. Énoncez les incohérences entre les interfaces
Implémentez les fonctions de rappel de synchronisation d'état
Utilisez des variables globales partagées pour le suivi de l'état
Appelez les fonctions de synchronisation après des changements d'état majeurs
3. Problèmes de performance avec plusieurs interfaces
Réduire les fréquences de mise à jour pour les interfaces non critiques
Implémenter des mises à jour sélectives en fonction de l'interface active
Envisager la désactivation des interfaces inutilisées pour des projets spécifiques
4. Limites de mémoire
Surveillez la mémoire RAM disponible avec Serial.print(freeMemory())
Désactivez les interfaces inutilisées si la mémoire est insuffisante
Optimisez les fonctions de rappel pour minimiser l'utilisation de mémoire
void debugSystemState() {
Serial.println("=== System State Debug ===");
Serial.println("Free Memory: " + String(freeMemory()) + " bytes");
Serial.println("Digital Pins:");
for (int pin = 0; pin <= 13; pin++) {
if (webDigitalPinsPage.isPinEnabled(pin)) {
Serial.println(" Pin " + String(pin) + ": " + String(pinStates[pin] ? "HIGH" : "LOW"));
}
}
Serial.println("Sliders: " + String(currentSlider1) + ", " + String(currentSlider2));
Serial.println("Joystick: X=" + String(currentJoystickX) + ", Y=" + String(currentJoystickY));
Serial.println("========================");
}
Après avoir maîtrisé l'exemple MultipleWebApps :
Personnalisez votre projet: Supprimez les interfaces inutilisées et ajoutez une logique spécifique au projet
Ajouter des capteurs: Intégrez de vraies lectures de capteurs pour la surveillance des entrées
Implémenter la sécurité: Ajouter des arrêts d'urgence et des dispositifs d'interverrouillage de sécurité
Créer des commandes personnalisées: Étendre l’interface de chat avec des commandes spécifiques au projet
Ajouter la journalisation des données: Utiliser le moniteur Web pour le stockage permanent des données
Optimisation mobile: Tester et optimiser l'utilisation sur les appareils mobiles
Pour obtenir de l'aide supplémentaire :
Consultez la documentation des exemples individuels (Chat_Example.txt, WebMonitor_Example.txt, etc.)
Consultez la documentation de référence de l'API
Consultez les tutoriels DIYables : https://newbiely.com/tutorials/arduino-uno-r4/arduino-uno-r4-diyables-webapps
Forums de la communauté Arduino
Cet exemple complet constitue la base de pratiquement n'importe quel projet Arduino contrôlé via le Web. Commencez avec ce modèle et adaptez-le à vos besoins spécifiques !