Arduino UNO R4 plusieurs boutons
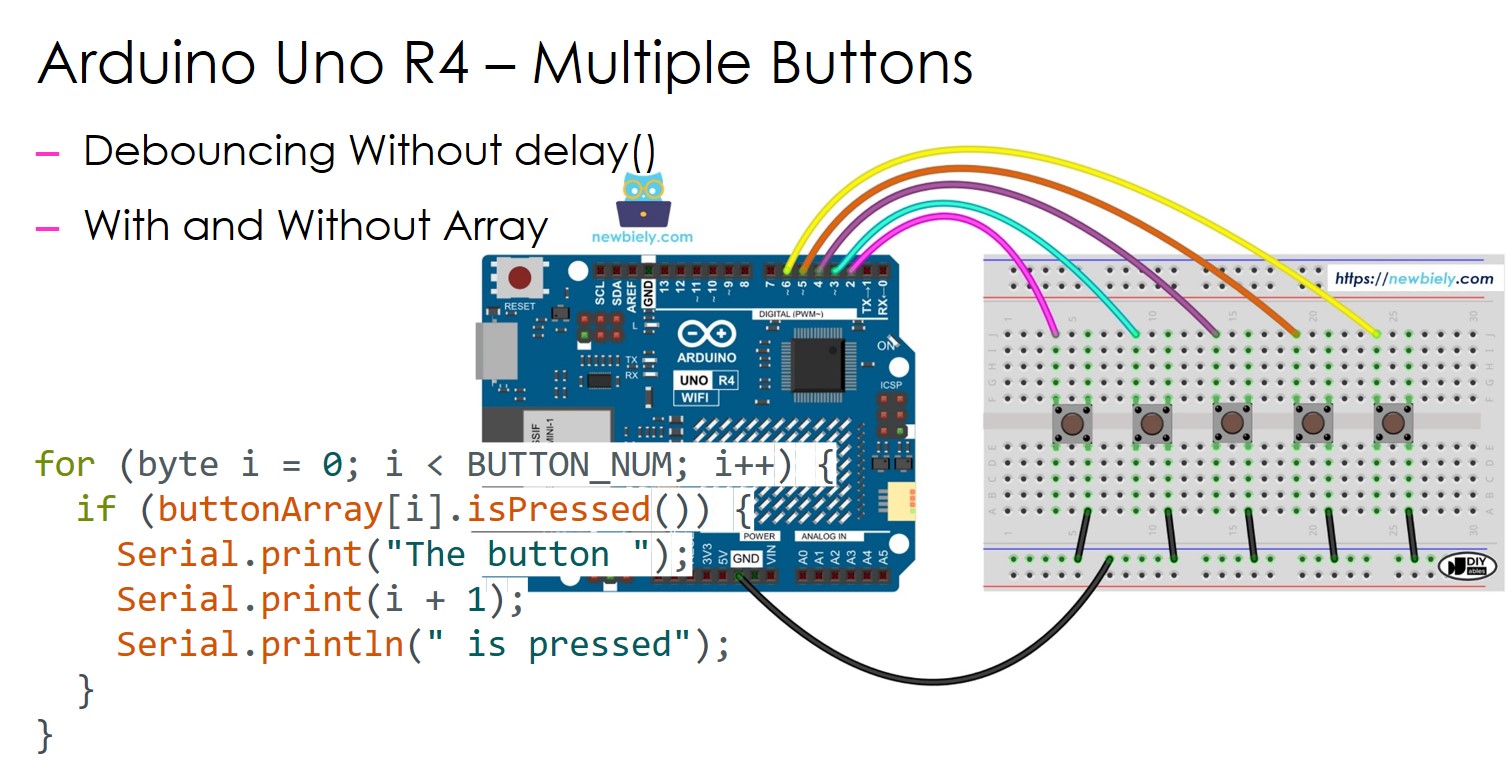
Ce guide vous montre comment utiliser un Arduino UNO R4 avec plusieurs boutons en même temps sans la fonction delay() pour l’anti-rebond. Le guide propose du code selon deux méthodes différentes :
- Code Arduino UNO R4 qui gère le rebond de plusieurs boutons sans utiliser la fonction delay().
- Code Arduino UNO R4 qui gère le rebond de plusieurs boutons en utilisant des tableaux sans utiliser la fonction delay().
Nous utiliserons cinq boutons comme exemples. Vous pouvez facilement changer cela pour deux boutons, quatre boutons ou même plus.
Préparation du matériel
Ou vous pouvez acheter les kits suivants:
| 1 | × | Kit de Démarrage DIYables STEM V4 IoT (Arduino inclus) | |
| 1 | × | Kit de Capteurs DIYables (30 capteurs/écrans) | |
| 1 | × | Kit de Capteurs DIYables (18 capteurs/écrans) |
Bouton À propos
Nous proposons un guide détaillé sur les boutons, couvrant les connexions matérielles, leur fonctionnement, le câblage avec Arduino UNO R4 et la manière d’écrire le code. En savoir plus ici :
- Arduino UNO R4 - Bouton. tutorial
Diagramme de câblage
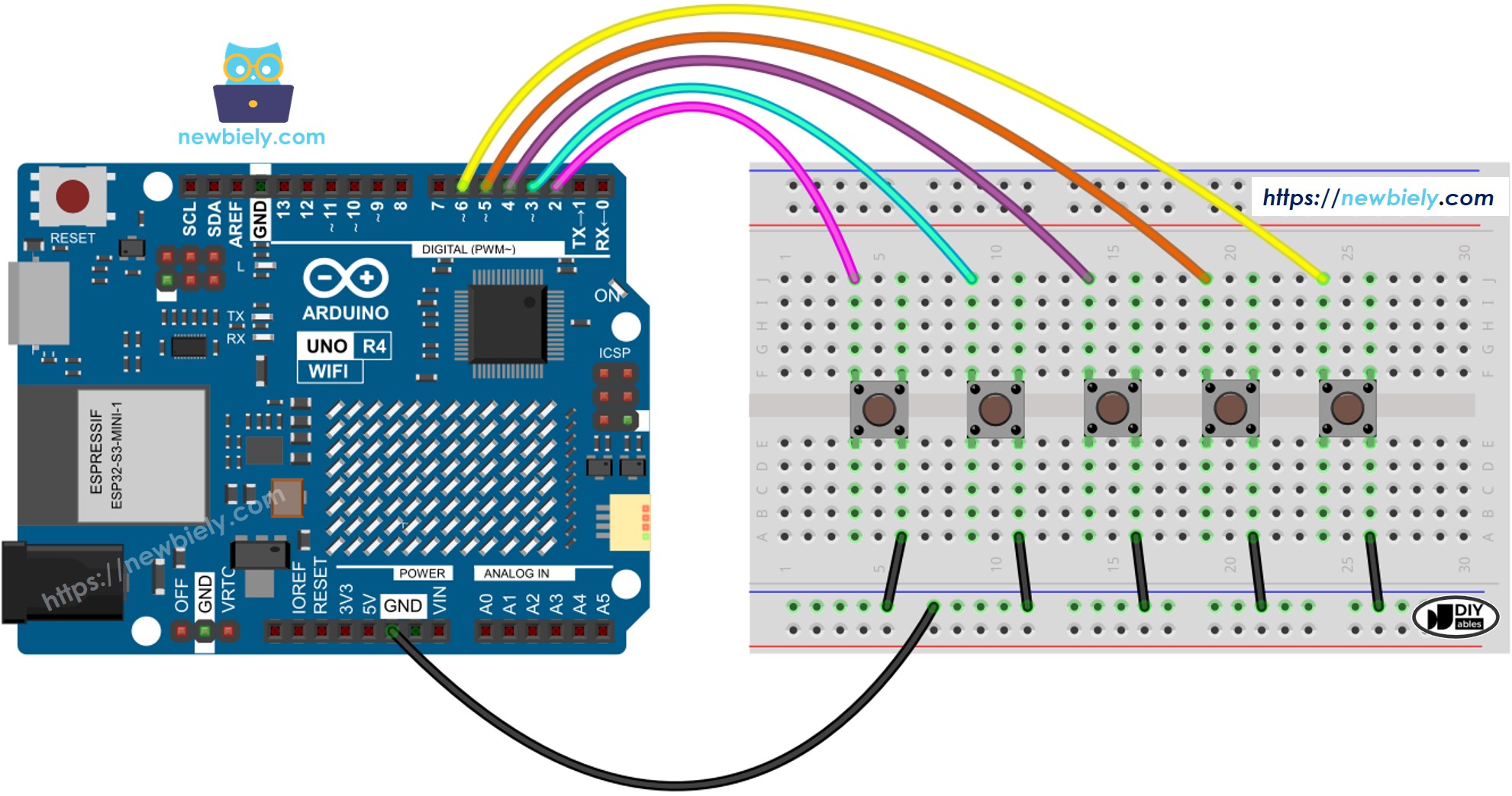
Cette image a été créée avec Fritzing. Cliquez pour agrandir l'image.
Code Arduino UNO R4 - Plusieurs boutons avec anti-rebond
Lorsque l'on utilise plusieurs boutons, les situations peuvent devenir complexes.
*Applications qui nécessitent un anti-rebond des boutons
*Applications qui doivent identifier quand les boutons sont pressés ou relâchés
La bibliothèque ezButton simplifie le travail avec les boutons en gérant l'anti-rebond et les événements des boutons en interne. Les utilisateurs n'ont pas à se soucier de la gestion des horodatages et des variables lors de l'utilisation de cette bibliothèque. De plus, l'utilisation de plusieurs boutons peut rendre le code plus clair et plus court.
Étapes rapides
Suivez ces instructions étape par étape :
- Si c’est la première fois que vous utilisez l'Arduino Uno R4 WiFi/Minima, reportez-vous au tutoriel sur Arduino UNO R4 - Installation du logiciel..
- Connectez l'Arduino Uno R4 aux boutons conformément au schéma fourni.
- Connectez la carte Arduino Uno R4 à votre ordinateur à l’aide d’un câble USB.
- Ouvrez l’IDE Arduino sur votre ordinateur.
- Sélectionnez la carte Arduino Uno R4 appropriée (par exemple, Arduino Uno R4 WiFi) et le port COM.
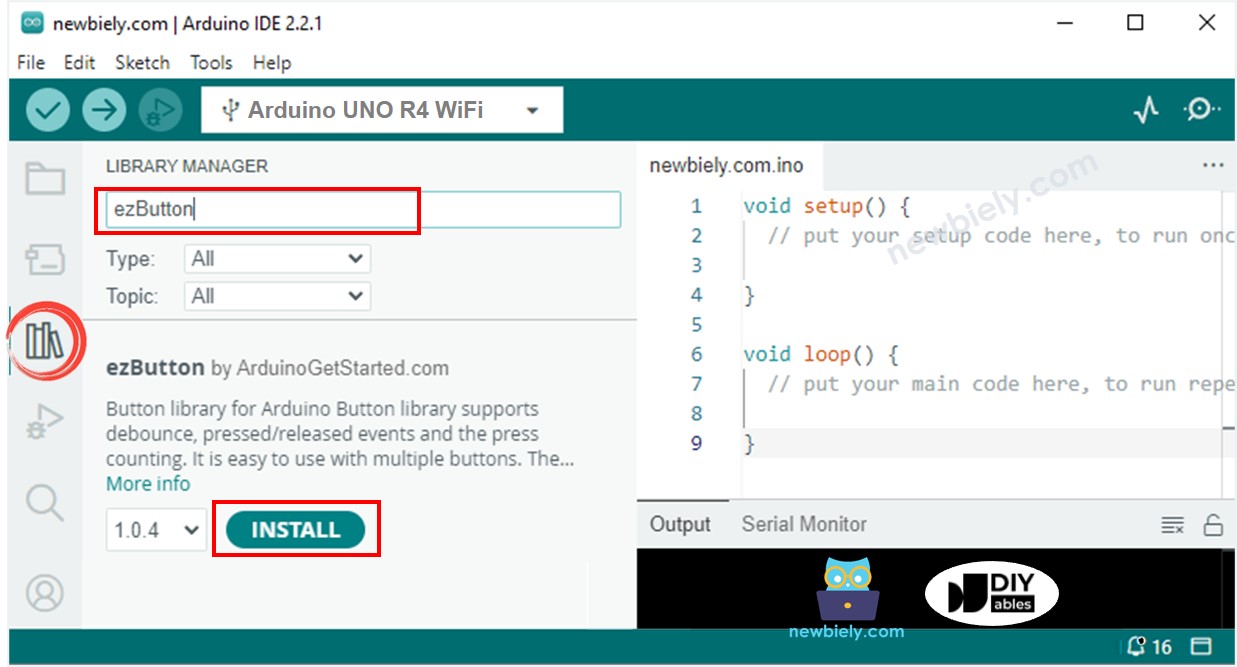
- Cliquez sur l’icône Libraries sur le côté gauche de l’IDE Arduino.
- Recherchez ezButton et localisez la bibliothèque de boutons créée par ArduinoGetStarted.com.
- Cliquez sur le bouton Install pour installer la bibliothèque ezButton.
- Copiez le code et collez-le dans l'IDE Arduino.
- Cliquez sur le bouton Upload dans l'IDE Arduino pour compiler et téléverser le code sur la carte Arduino UNO R4.
- Ouvrez le moniteur série dans l'IDE Arduino.
- Appuyez sur chaque bouton et relâchez-le, l'un après l'autre.
Arduino UNO R4 Code - Plusieurs boutons utilisant un tableau
Nous pouvons améliorer le code ci-dessus en utilisant un tableau de boutons.
