Raspberry Pi Pico - OLED 128×32
Ce tutoriel vous explique comment utiliser un Raspberry Pi Pico avec un écran OLED I2C 128x32. Vous allez apprendre :
- Comment connecter un écran OLED 128x32 au Raspberry Pi Pico.
- Comment afficher du texte et des chiffres sur l'écran OLED 128x32 avec le Raspberry Pi Pico.
- Comment dessiner sur l'écran OLED 128x32 avec le Raspberry Pi Pico.
- Comment afficher des images sur l'écran OLED 128x32 en utilisant le Raspberry Pi Pico.
- Comment aligner le texte et les chiffres au milieu de l'écran OLED 128x32.
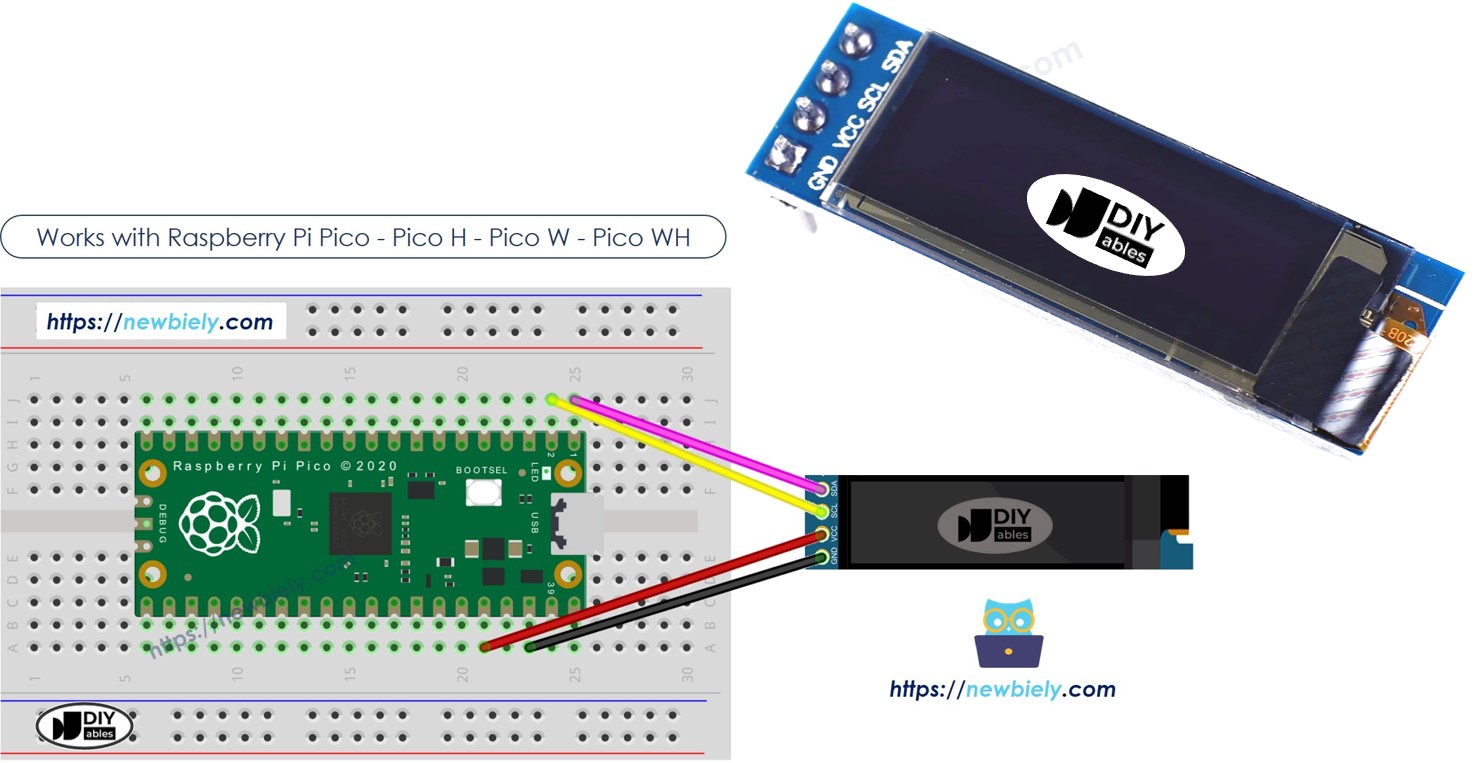
Préparation du matériel
| 1 | × | Raspberry Pi Pico W | |
| 1 | × | Raspberry Pi Pico Alternativement: | |
| 1 | × | Câble Micro USB | |
| 1 | × | Écran OLED I2C SSD1306 128x32 | |
| 1 | × | Fils de connexion | |
| 1 | × | Recommandé: Carte d'extension à bornier à vis pour Raspberry Pi Pico |
Ou vous pouvez acheter les kits suivants:
| 1 | × | Kit de Capteurs DIYables (30 capteurs/écrans) | |
| 1 | × | Kit de Capteurs DIYables (18 capteurs/écrans) |
À propos de l'écran OLED
Brochage de l'écran OLED I2C
- Broche GND : Connectez-la à la masse du Raspberry Pi Pico.
- Broche VCC : Connectez-la à la broche 5 volts du Raspberry Pi Pico pour l'alimentation.
- Broche SCL : Il s'agit de la broche d'horloge pour la communication I2C.
- Broche SDA : Il s'agit de la broche de données pour la communication I2C.
※ Note:
La configuration des broches sur un module OLED peut varier selon le fabricant et le type de module. Regardez toujours et suivez les marquages sur le module OLED. Faites attention !
Ce guide est destiné à un écran OLED utilisant le pilote I2C SSD1306. Nous l'avons testé avec un écran OLED de DIYables et cela a très bien fonctionné sans aucun problème.
Diagramme de câblage
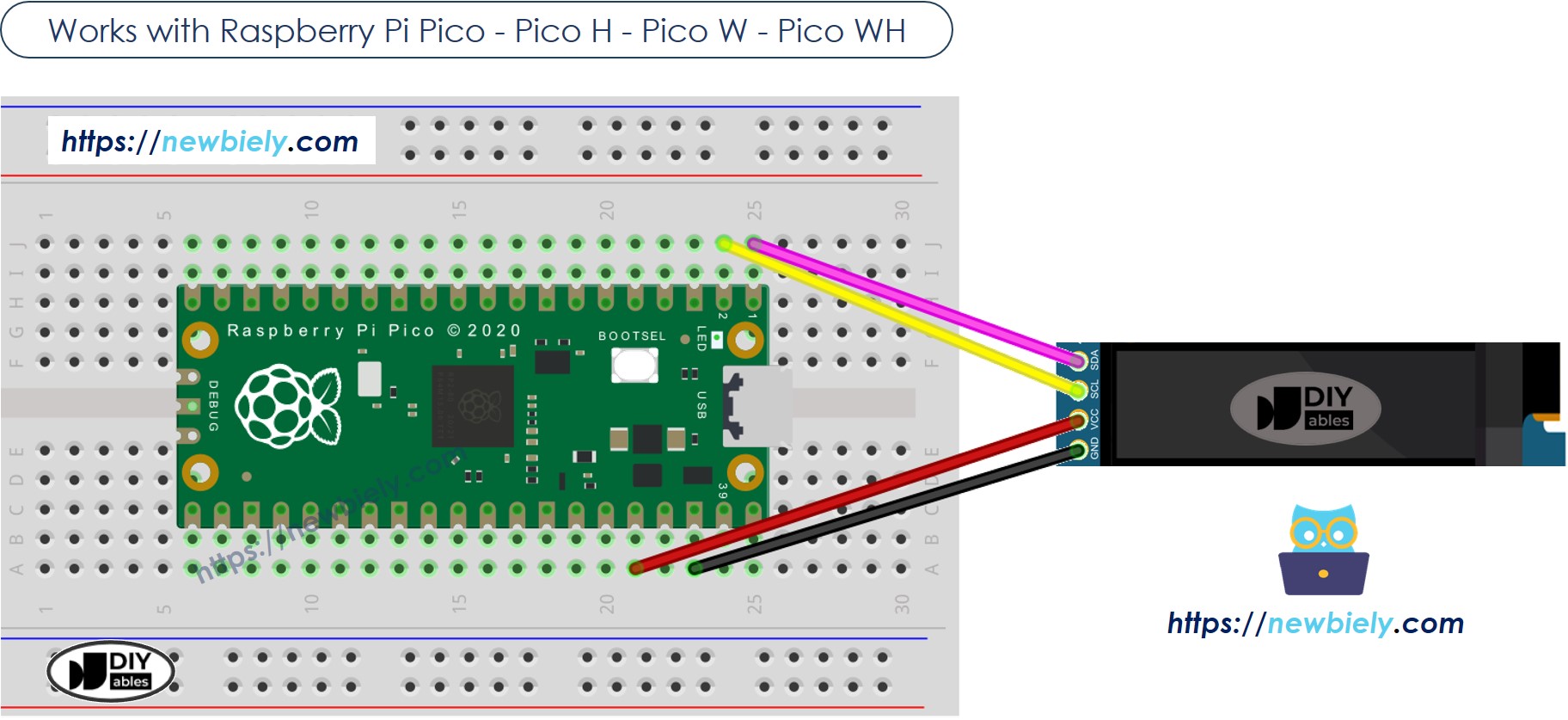
Cette image a été créée avec Fritzing. Cliquez pour agrandir l'image.
Ce qui suit est le tableau de câblage entre le module OLED 128x32 et le Raspberry Pi Pico.
| 128x32 OLED Module | Raspberry Pi Pico |
|---|---|
| VCC | 3.3V |
| GND | GND |
| SDA | GP0 |
| SCL | GP1 |
Code Raspberry Pi Pico - Afficher du texte, des nombres entiers et des nombres à virgule flottante sur un écran OLED
Étapes rapides
Veuillez suivre ces instructions étape par étape :
- Assurez-vous que l’IDE Thonny est installé sur votre ordinateur.
- Assurez-vous que le firmware MicroPython est installé sur votre Raspberry Pi Pico.
- Si c'est votre première utilisation d'un Raspberry Pico, reportez-vous au tutoriel Raspberry Pi Pico - Premiers pas. pour des instructions détaillées.
- Connectez l'écran OLED au Raspberry Pi Pico selon le diagramme fourni.
- Connectez le Raspberry Pi Pico à votre ordinateur à l’aide d’un câble USB.
- Lancez l’IDE Thonny sur votre ordinateur.
- Sur l’IDE Thonny, sélectionnez l’interpréteur MicroPython (Raspberry Pi Pico) en accédant à Outils Options.
- Dans l’onglet Interpréteur, sélectionnez MicroPython (Raspberry Pi Pico) dans le menu déroulant.
- Assurez-vous que le port correct est sélectionné. L’IDE Thonny devrait détecter automatiquement le port, mais vous devrez peut-être le sélectionner manuellement (par exemple COM3 sur Windows ou /dev/ttyACM0 sur Linux).
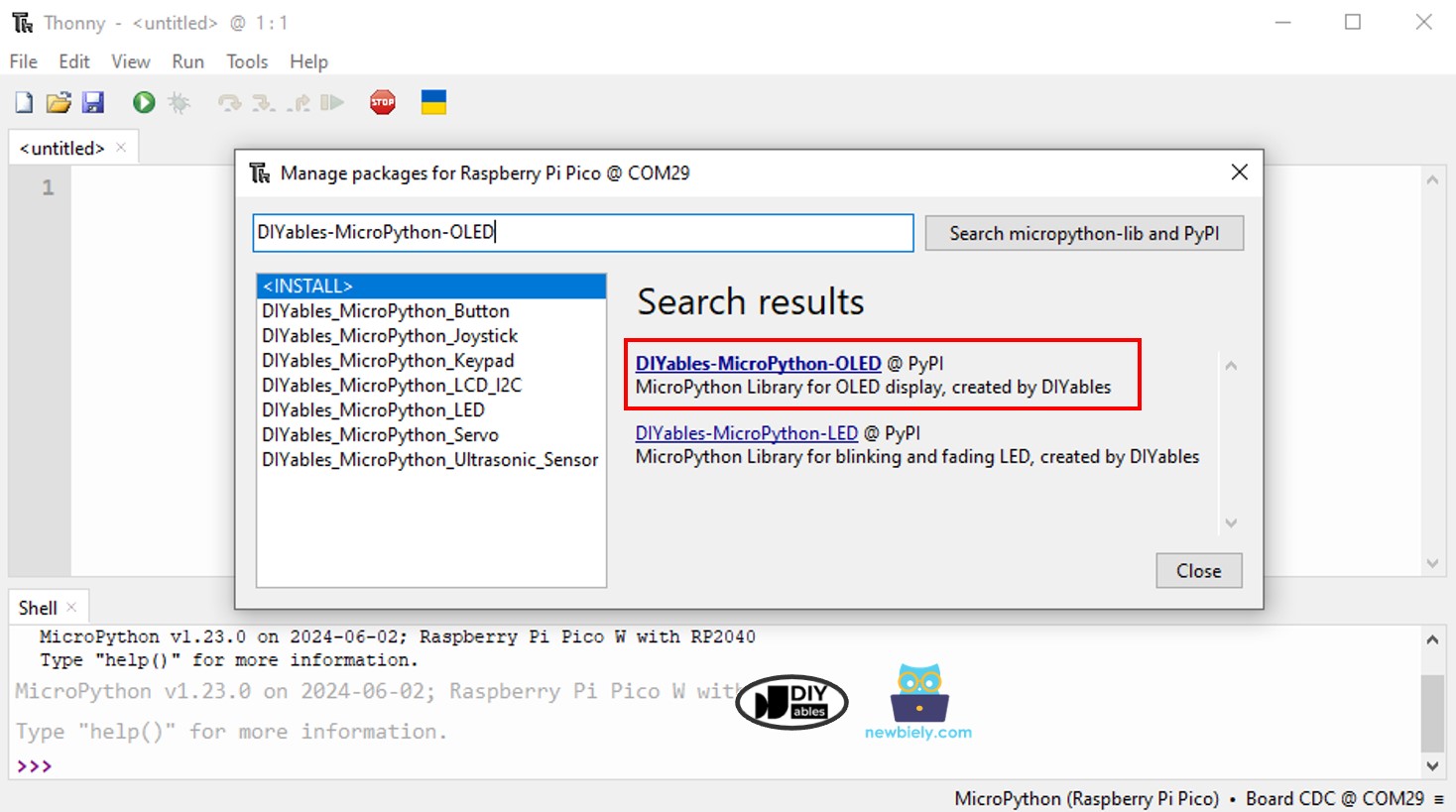
- Accédez à Outils Gérer les paquets sur l’IDE Thonny.
- Recherchez “DIYables-MicroPython-OLED”, puis trouvez la bibliothèque OLED créée par DIYables.
- Cliquez sur DIYables-MicroPython-OLED, puis cliquez sur le bouton Install pour installer la bibliothèque OLED.
- Copiez le code ci-dessus et collez-le dans l'éditeur de Thonny IDE.
- Enregistrez le script sur votre Raspberry Pi Pico en procédant comme suit :
- Cliquez sur le bouton Enregistrer, ou utilisez les touches Ctrl+S.
- Dans la boîte de dialogue d'enregistrement, vous verrez deux sections : Cet ordinateur et Raspberry Pi Pico. Sélectionnez Raspberry Pi Pico.
- Enregistrez le fichier sous main.py.
- Cliquez sur le bouton vert Exécuter (ou appuyez sur F5) pour lancer le script. Le script s'exécutera.
- Jetez un œil sur l'écran OLED. Cela ressemble à ce qui suit :
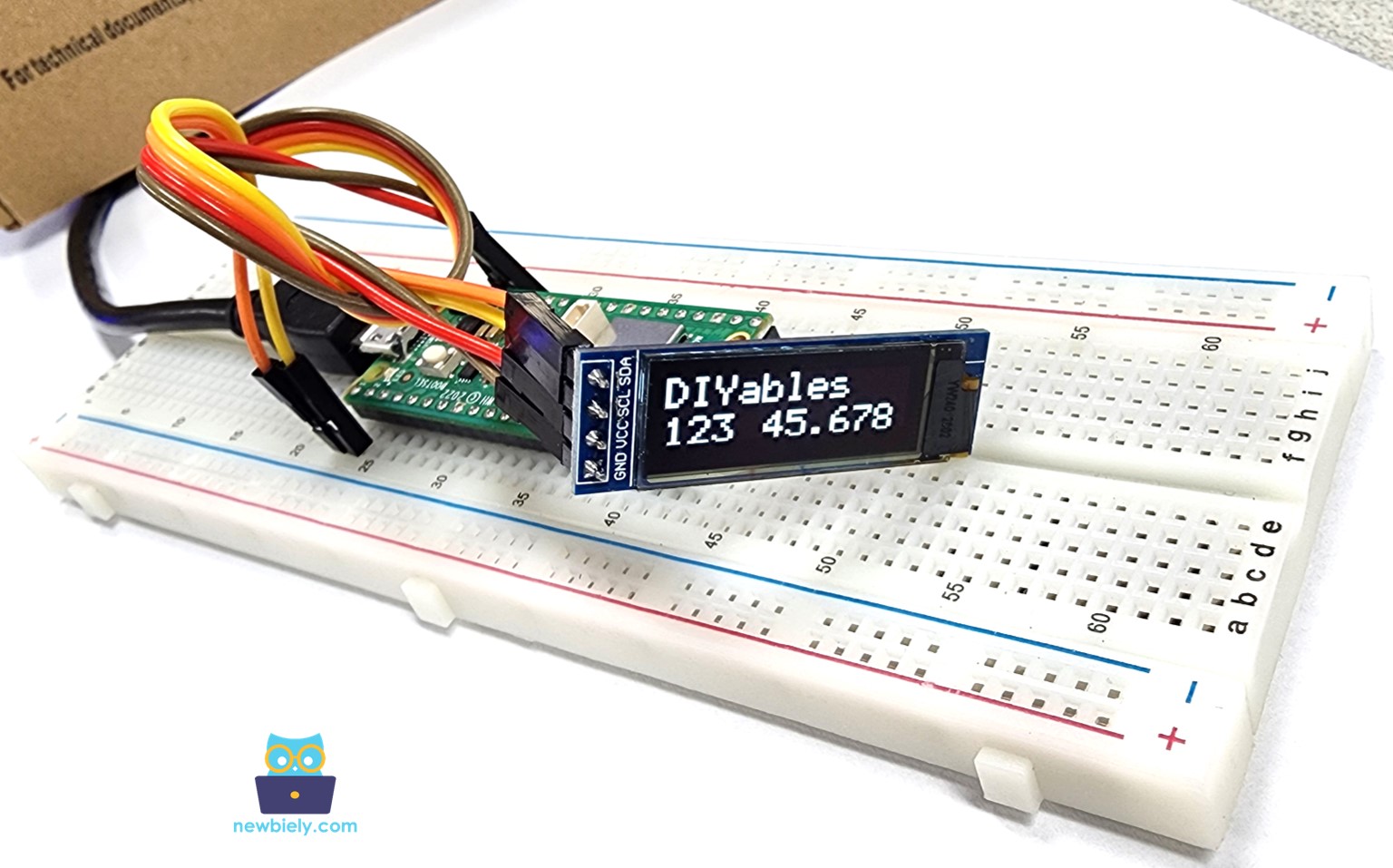
Code Raspberry Pi Pico - Dessiner sur l'OLED
Lorsque vous exécutez le code ci-dessus, un rectangle, un cercle et un triangle apparaîtront sur l'écran OLED, comme montré ci-dessous.

Code pour Raspberry Pi Pico – Afficher une image sur OLED
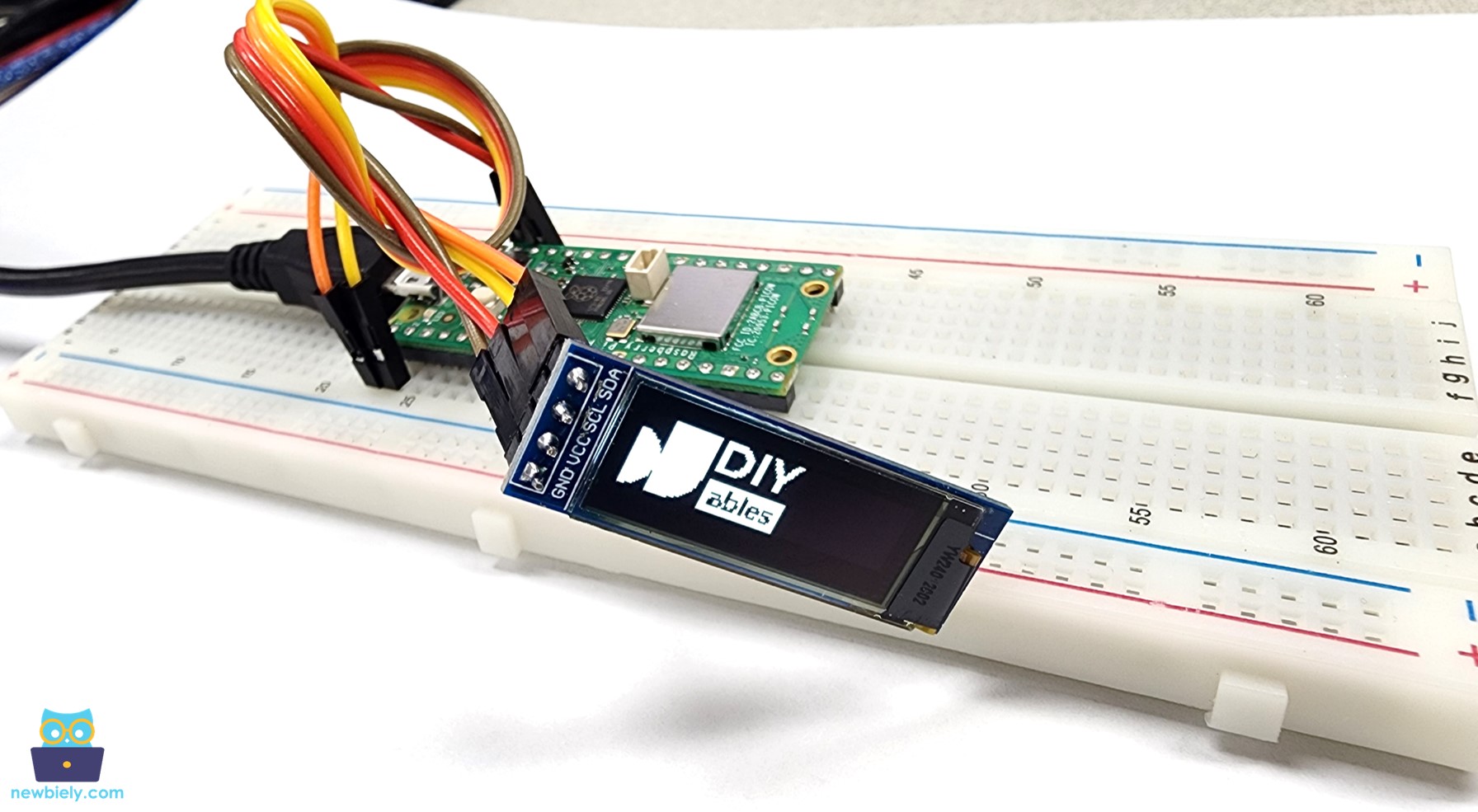
Le code ci-dessous dessine une image sur l'écran LCD. L'image est l'icône DIYables.
Lorsque vous exécutez le code ci-dessus, l'image apparaîtra sur l'écran OLED, comme indiqué ci-dessous.
Pour afficher une image différente sur l'écran OLED, suivez ces étapes :
- Convertissez l'image (dans n'importe quel format) en un tableau bitmap. Vous pouvez utiliser cet outil en ligne pour la conversion. Reportez-vous à l'image ci-dessous pour savoir comment convertir une image en un tableau bitmap. Dans cet exemple, j'ai converti l'icône Raspberry Pi Pico en un tableau bitmap.*
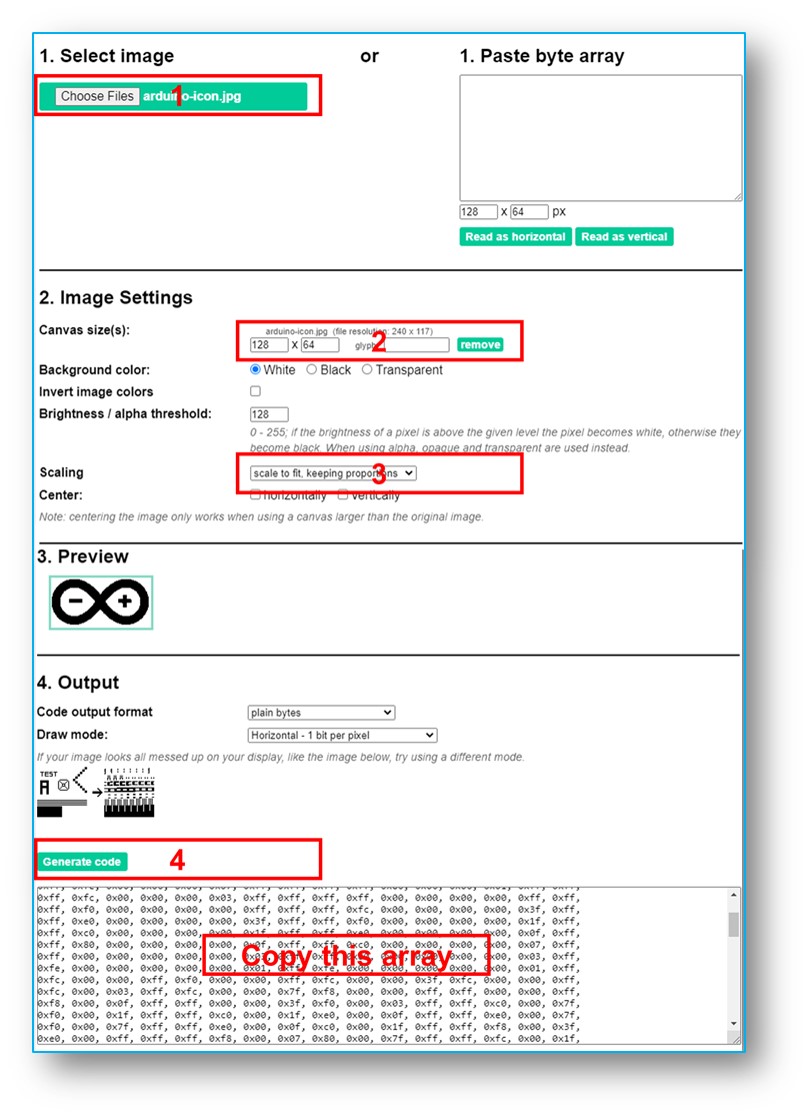
- Remplacez le tableau bitmap existant dans le code de votre Raspberry Pi Pico par le nouveau tableau converti.
- Ajustez la largeur et la hauteur de l'image dans le code de votre Raspberry Pi Pico pour qu'elles correspondent aux dimensions de la nouvelle image.
Remarque : Assurez-vous que la taille de l'image est égale ou inférieure à celle de l'écran OLED.
Comment centrer automatiquement verticalement et horizontalement le texte et les chiffres sur un écran OLED
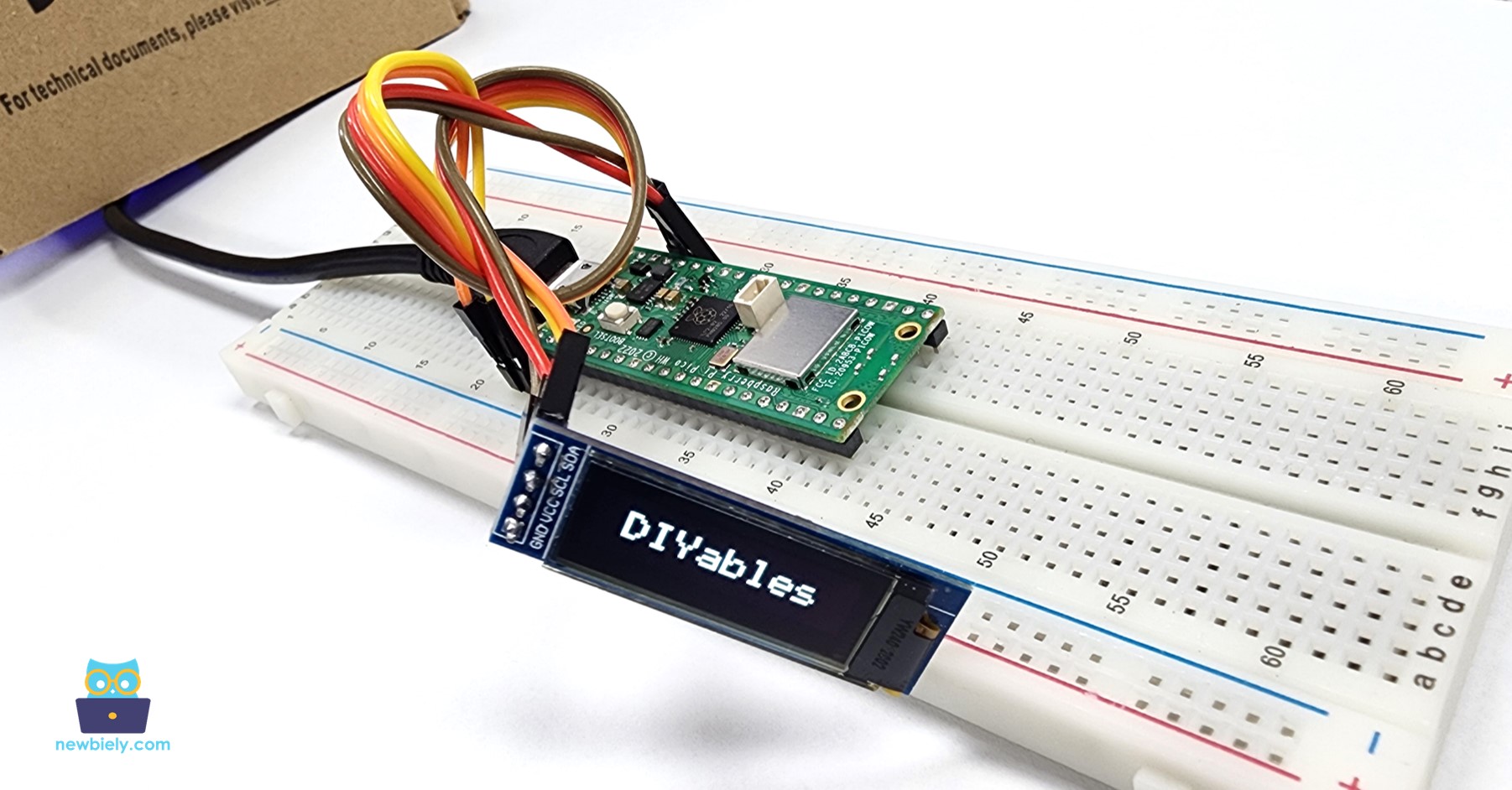
Le code MicroPython ci-dessous centre automatiquement le texte à la fois verticalement et horizontalement sur l'écran OLED.
Après avoir exécuté le code, le texte sera centré à la fois verticalement et horizontalement sur l'écran OLED.
Dépannage des écrans OLED
Si rien n'est affiché sur l'écran OLED 128×32, veuillez essayer les étapes suivantes :
- Vérifiez que toutes les connexions de câblage sont correctes.
- Assurez-vous que votre OLED I2C utilise un pilote SSD1306.
- Déterminez l’adresse I2C de votre OLED en exécutant le code du scanner d’adresses I2C sur un Raspberry Pi Pico.
Sortie dans le Shell en bas de Thonny :
