ESP8266 - Capteur de Température et d'Humidité - OLED
Ce tutoriel vous explique comment utiliser l'ESP8266 pour lire la température et l'humidité à partir du capteur DHT11/DHT22 et les afficher sur un OLED.
Préparation du matériel
You can use DHT22 sensor instead of DHT11 sensor.
| 1 | × | Recommandé: Carte d'extension à bornier à vis pour ESP8266 | |
| 1 | × | Recommandé: Répartiteur d'alimentation pour ESP8266 Type-C |
Ou vous pouvez acheter les kits suivants:
| 1 | × | Kit de Capteurs DIYables (30 capteurs/écrans) | |
| 1 | × | Kit de Capteurs DIYables (18 capteurs/écrans) |
À propos de l'écran OLED, des capteurs d'humidité et de température DHT11 et DHT22
Si vous n'êtes pas familiarisé avec l'écran OLED, les capteurs de température et d'humidité DHT11 et DHT22 (y compris le brochage, les fonctionnalités, la programmation, etc.), les tutoriels suivants peuvent vous aider :
- ESP8266 - OLED. tutorial
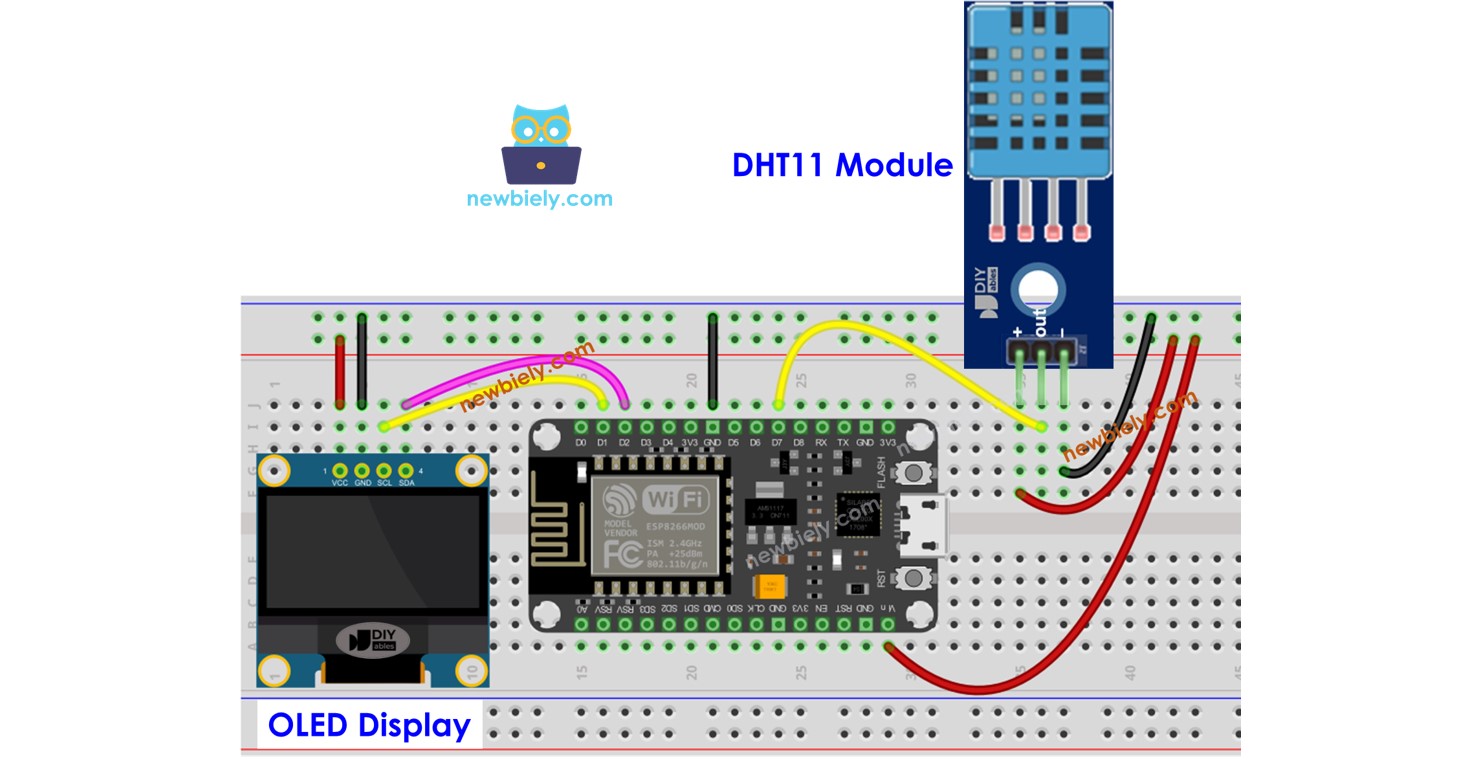
Diagramme de câblage
Câblage ESP8266 - Module DHT11 LCD
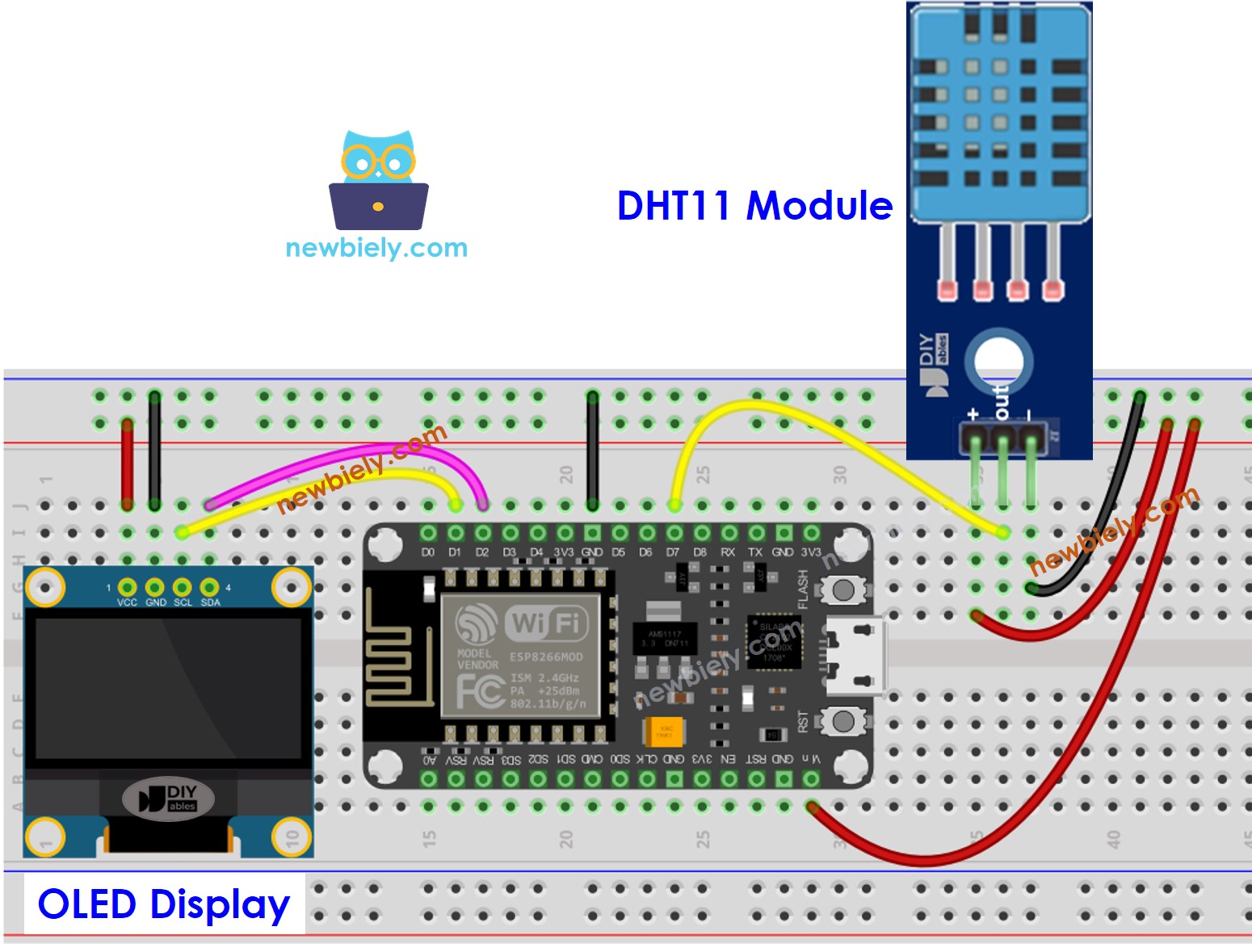
Cette image a été créée avec Fritzing. Cliquez pour agrandir l'image.
Pour plus d'informations, consultez Brochage ESP8266. et Comment alimenter l'ESP8266..
ESP8266 - Câblage du module DHT22 avec LCD
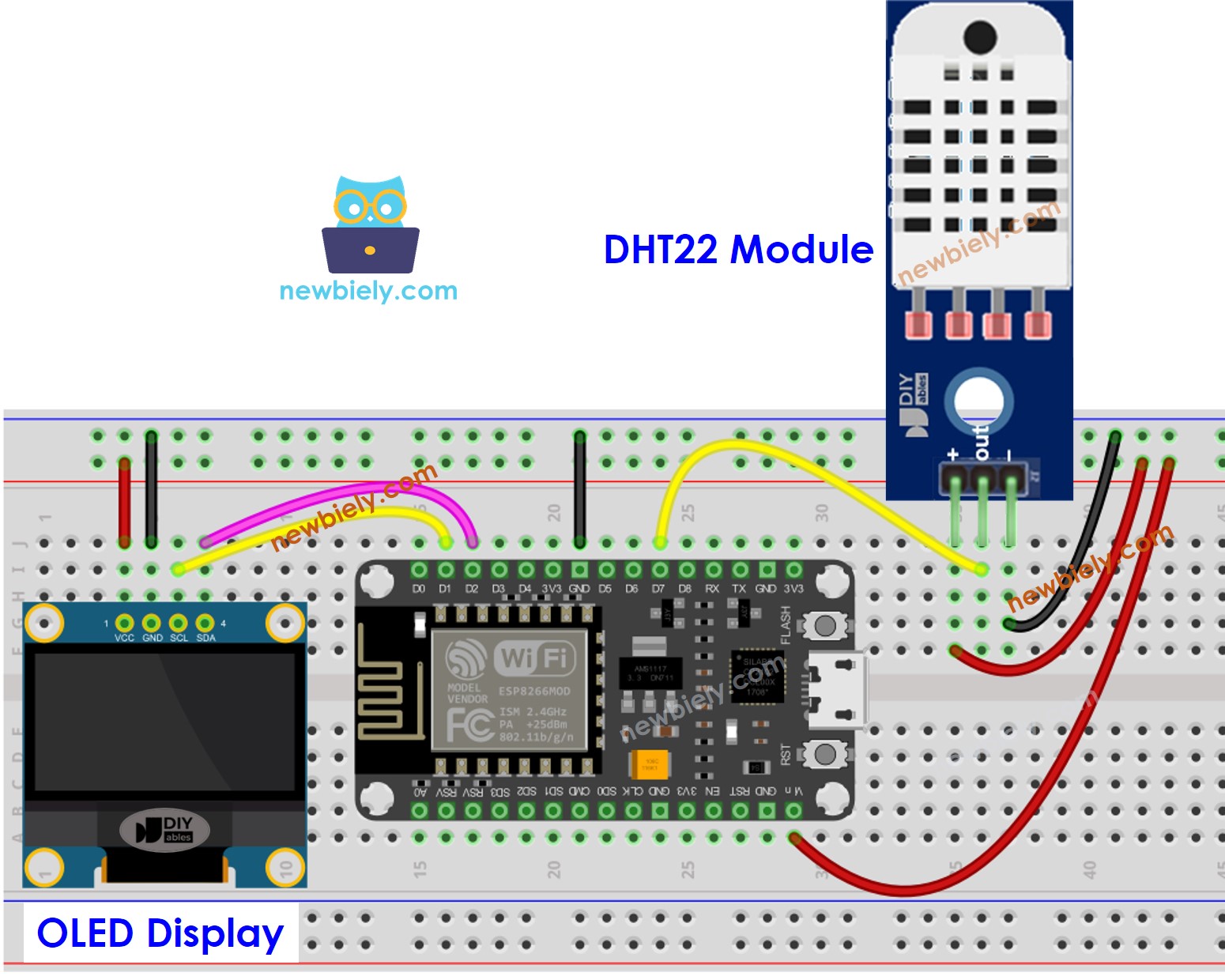
Cette image a été créée avec Fritzing. Cliquez pour agrandir l'image.
Code ESP8266 - Capteur DHT11 - OLED
Étapes rapides
Pour commencer avec l'ESP8266 sur Arduino IDE, suivez ces étapes :
- Consultez le tutoriel Installation du logiciel ESP8266. si c'est la première fois que vous utilisez ESP8266.
- Câblez les composants comme indiqué sur le schéma.
- Connectez la carte ESP8266 à votre ordinateur à l'aide d'un câble USB.
- Ouvrez Arduino IDE sur votre ordinateur.
- Choisissez la bonne carte ESP8266, telle que (par exemple NodeMCU 1.0 (Module ESP-12E)), et son port COM respectif.
- Cliquez sur l'icône Libraries dans la barre gauche de l'Arduino IDE.
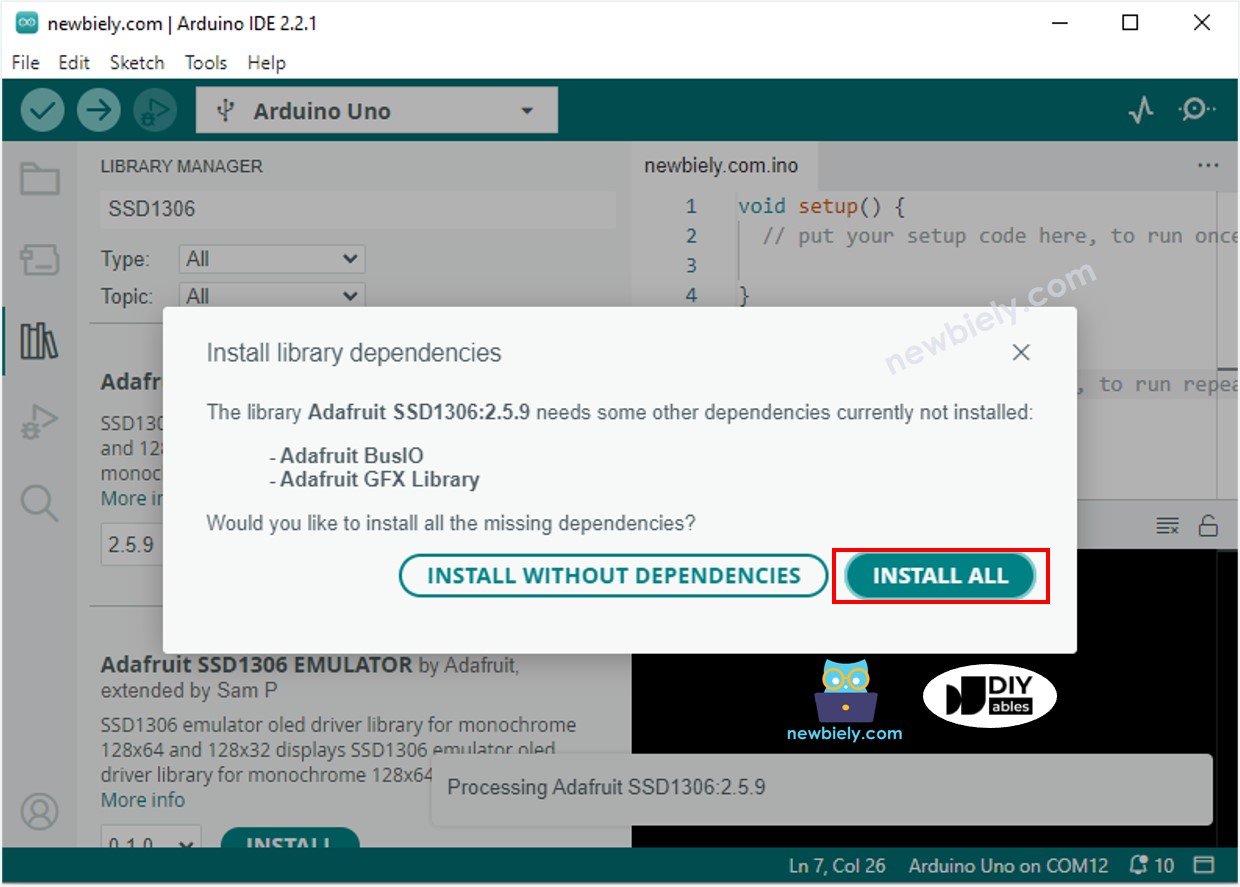
- Recherchez “SSD1306” et localisez la bibliothèque SSD1306 d'Adafruit.
- Ensuite, appuyez sur le bouton Install pour terminer l'installation.
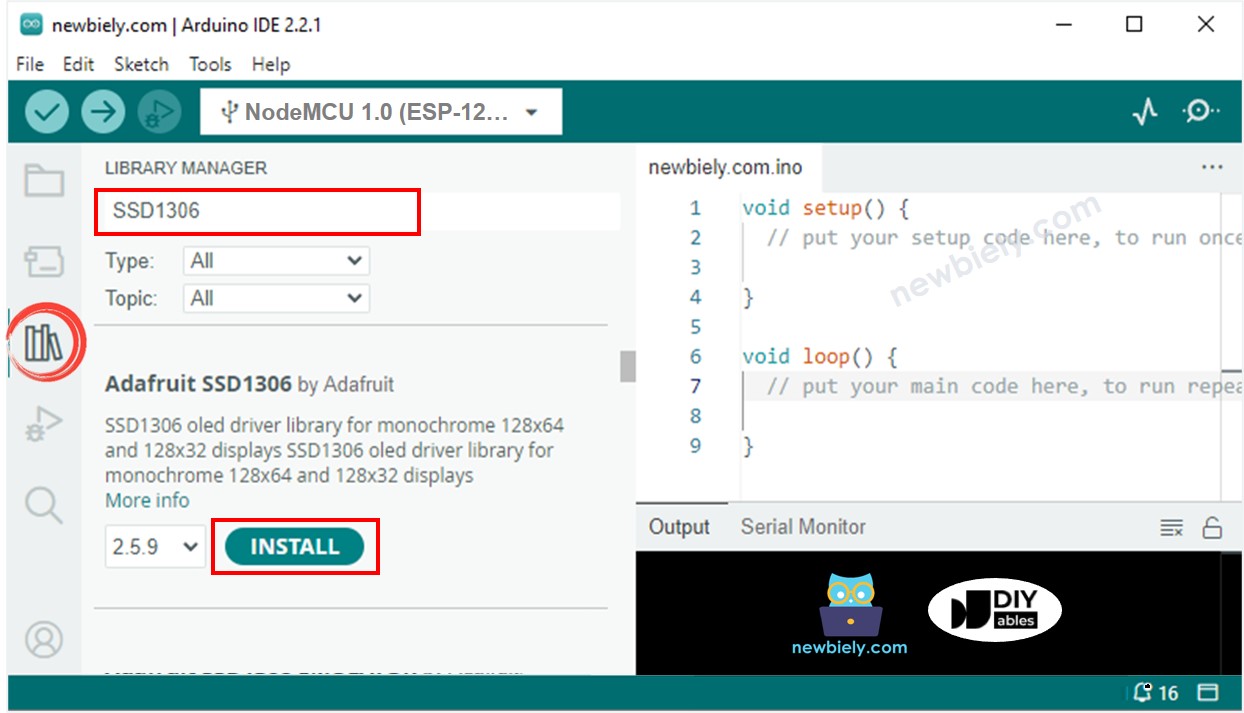
- Vous serez invité à installer des dépendances de bibliothèque supplémentaires.
- Pour les installer toutes, cliquez sur le bouton Install All.
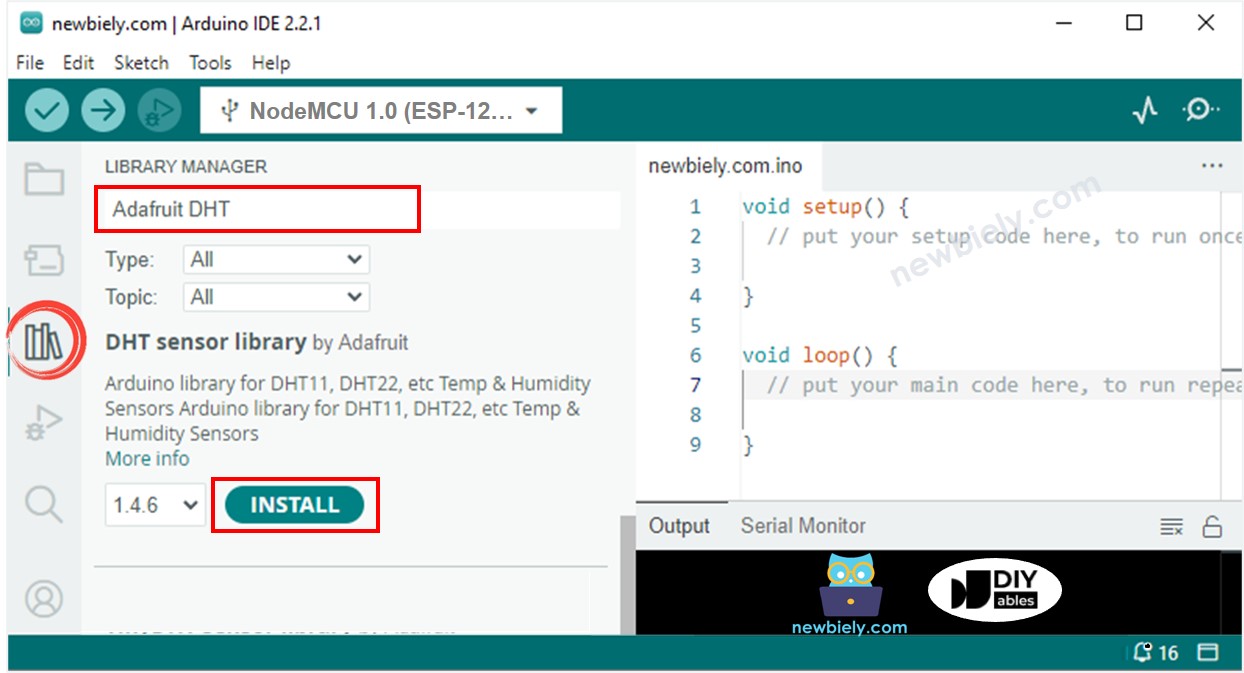
- Recherchez « DHT » et localisez la bibliothèque de capteurs DHT par Adafruit.
- Appuyez sur le bouton Install pour installer la bibliothèque.
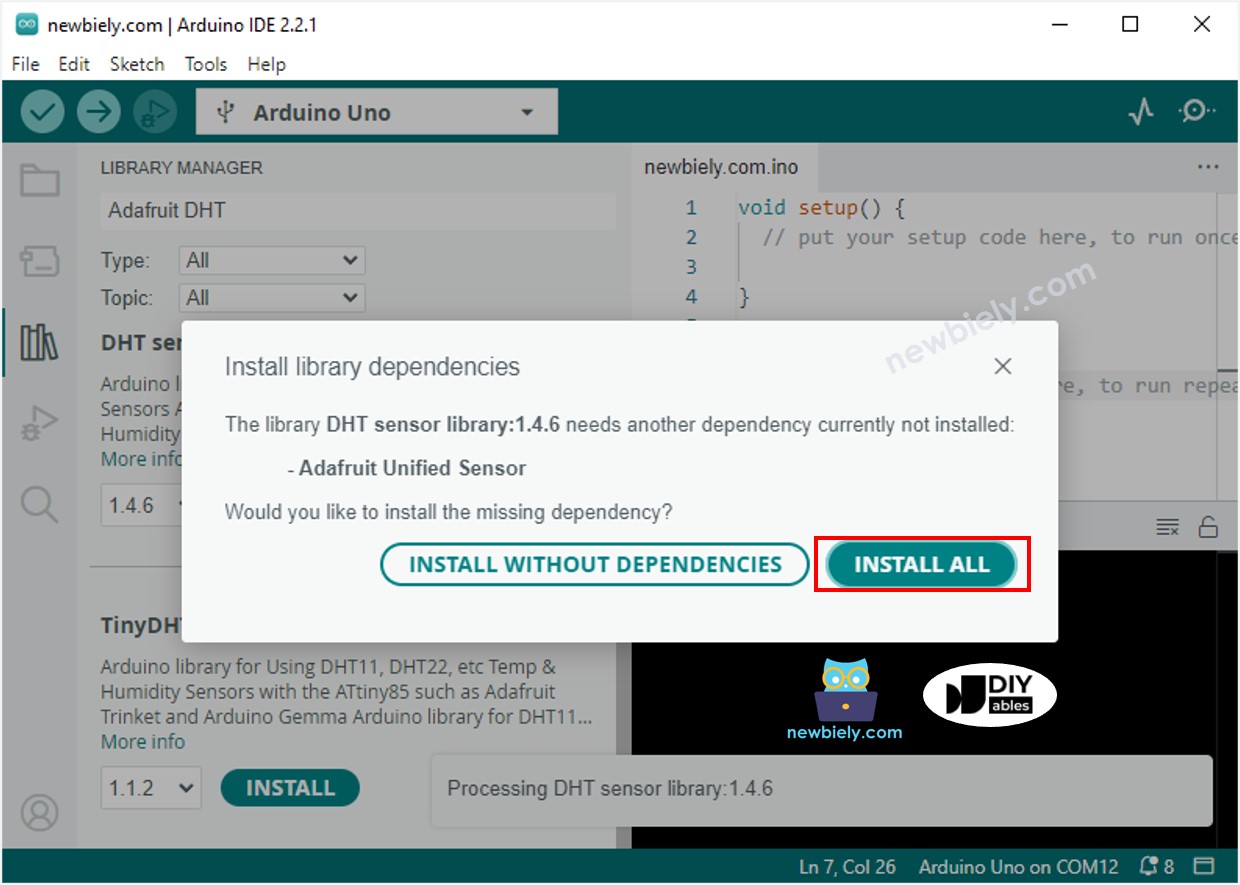
- Vous devrez installer d'autres dépendances de bibliothèques.
- Cliquez sur le bouton Install All pour installer toutes les dépendances de la bibliothèque.
- Copiez le code et ouvrez-le avec l'IDE Arduino.
- Cliquez sur le bouton Upload dans l'IDE Arduino pour compiler et téléverser le code vers l'ESP8266.
- Placez le capteur dans de l'eau chaude et de l'eau froide, ou tenez-le dans votre main.
- Consultez le résultat sur l'écran OLED et dans le moniteur série.
※ Note:
Le code en question centrera le texte à la fois horizontalement et verticalement sur un écran OLED.
Code ESP8266 - Capteur DHT22 - OLED
※ Note:
Le code pour le DHT11 et le DHT22 est le même, à l'exception d'une seule ligne. La bibliothèque pour les deux est également la même.
