Raspberry Pi - Capteur à ultrasons - Buzzer piézoélectrique
Ce tutoriel vous explique comment utiliser un Raspberry Pi et un capteur ultrasonique pour contrôler un buzzer piézoélectrique. En détail :
- Le Raspberry Pi produit un son lorsque l'objet est proche du capteur ultrasonique.
- Le Raspberry Pi interrompt le son lorsque l'objet est éloigné du capteur ultrasonique.
- Le Raspberry Pi joue une mélodie lorsque l'objet est proche du capteur ultrasonique.
Préparation du matériel
Ou vous pouvez acheter les kits suivants:
| 1 | × | Kit de Capteurs DIYables (30 capteurs/écrans) | |
| 1 | × | Kit de Capteurs DIYables (18 capteurs/écrans) |
À propos du Buzzer Piézoélectrique et du Capteur Ultrasonique
Si vous n'êtes pas familier avec le buzzer piézoélectrique et le capteur ultrasonique (y compris le brochage, le fonctionnement et la programmation), les tutoriels suivants peuvent vous fournir plus d'informations :
Diagramme de câblage
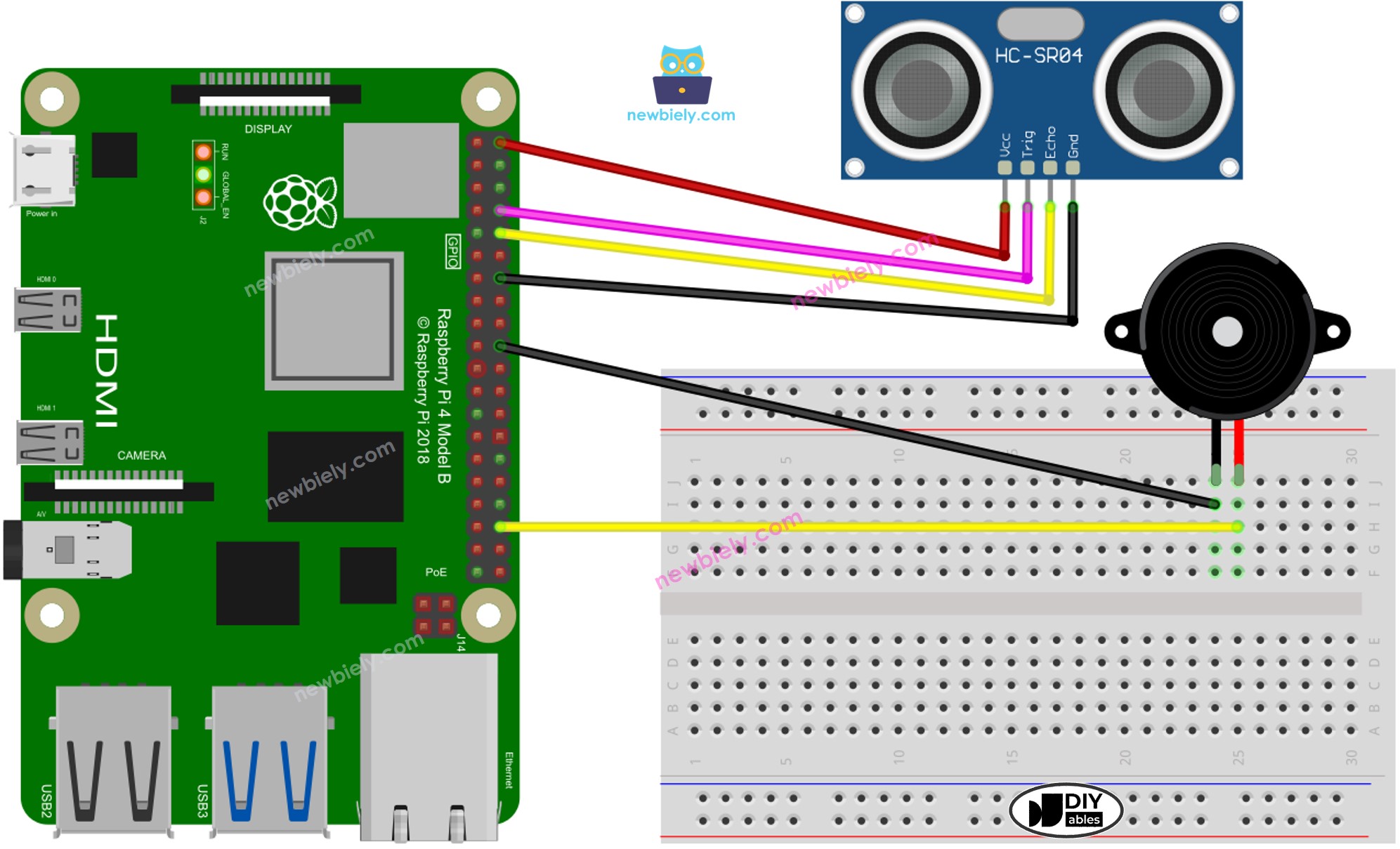
Cette image a été créée avec Fritzing. Cliquez pour agrandir l'image.
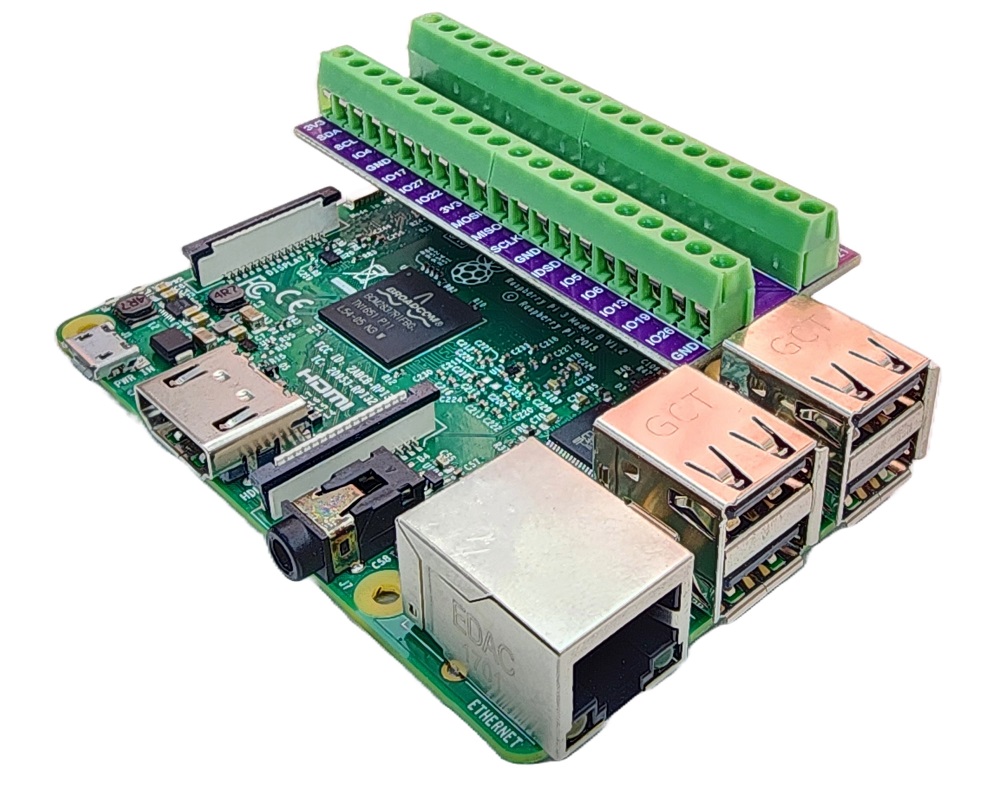
Pour simplifier et organiser votre montage de câblage, nous recommandons l'utilisation d'un shield à bornier à vis pour Raspberry Pi. Ce shield assure des connexions plus sûres et mieux gérées, comme illustré ci-dessous :
Code Raspberry Pi - Son Simple
Dans cette section, nous programmerons le Raspberry Pi pour faire en sorte qu'un buzzer piézo génère un son simple chaque fois que la distance mesurée par le capteur ultrasonique est inférieure à un seuil.
Étapes rapides
- Assurez-vous d'avoir Raspbian ou tout autre système d'exploitation compatible avec Raspberry Pi installé sur votre Pi.
- Assurez-vous que votre Raspberry Pi est connecté au même réseau local que votre PC.
- Assurez-vous que votre Raspberry Pi est connecté à Internet si vous avez besoin d'installer des bibliothèques.
- Si c'est la première fois que vous utilisez Raspberry Pi, voyez Installation du logiciel - Raspberry Pi.
- Connectez votre PC au Raspberry Pi via SSH en utilisant le client SSH intégré sur Linux et macOS ou PuTTY sur Windows. Voyez comment connecter votre PC au Raspberry Pi via SSH.
- Assurez-vous que vous avez la bibliothèque RPi.GPIO installée. Sinon, installez-la en utilisant la commande suivante :
- Créez un fichier script Python ultrasonic_sensor_buzzer.py et ajoutez le code suivant :
- Enregistrez le fichier et exécutez le script Python en entrant la commande suivante dans le terminal :
- Agitez votre main devant le capteur.
- Écoutez le son du buzzer piezo.
Le script s'exécute dans une boucle infinie en continu jusqu'à ce que vous appuyiez sur Ctrl + C dans le terminal.
Explication du code
Consultez l'explication ligne par ligne contenue dans les commentaires du code source !
Raspberry Pi joue la mélodie de la chanson
Dans cette section, nous programmerons le Raspberry Pi pour déclencher un buzzer piézoélectrique afin de jouer la chanson "Jingle Bells" lorsque la distance est inférieure à un seuil.
Étapes rapides
- Créez un fichier de script Python ultrasonic_sensor_buzzer_Jingle_Bells.py et ajoutez le code suivant :
- Enregardez le fichier et exécutez le script Python en lançant la commande suivante dans le terminal :
- Déplacez votre main devant le capteur.
- Écoutez la mélodie jouée par le buzzer piézo.
Explication du code
Consultez l'explication ligne par ligne contenue dans les commentaires du code source !
