Raspberry Pi - GPS
Ce tutoriel vous apprend à utiliser un Raspberry Pi avec un module GPS NEO-6M. En détail, nous allons apprendre :
- Comment connecter un Raspberry Pi à un module GPS NEO-6M
- Comment programmer le Raspberry Pi pour lire les coordonnées GPS (longitude, latitude et altitude) à partir d'un module GPS NEO-6M
- Comment programmer le Raspberry Pi pour calculer la distance entre la position GPS actuelle et une coordonnée GPS prédéfinie (par exemple, les coordonnées de Londres).
Outre la longitude, la latitude et l'altitude, le Raspberry Pi est également capable de lire la vitesse GPS (km/h) et la date et l'heure à partir d'un module GPS NEO-6M.
Préparation du matériel
Ou vous pouvez acheter les kits suivants:
| 1 | × | Kit de Capteurs DIYables (30 capteurs/écrans) | |
| 1 | × | Kit de Capteurs DIYables (18 capteurs/écrans) |
À propos du module GPS NEO-6M
Module GPS NEO-6M est un module GPS qui peut fournir les informations suivantes :
- Longitude
- Latitude
- Altitude
- Vitesse GPS (km/h)
- Date et heure
Le brochage du module GPS NEO-6M
Le module GPS NEO-6M possède quatre broches :
- Broche VCC : Celle-ci doit être connectée au VCC (3,3V ou 5V)
- Broche GND : Celle-ci doit être connectée à GND (0V)
- Broche TX : Celle-ci est utilisée pour la communication série et doit être connectée à la broche RX série sur le Raspberry Pi.
- Broche RX : Celle-ci est utilisée pour la communication série et doit être connectée à la broche TX série sur le Raspberry Pi.
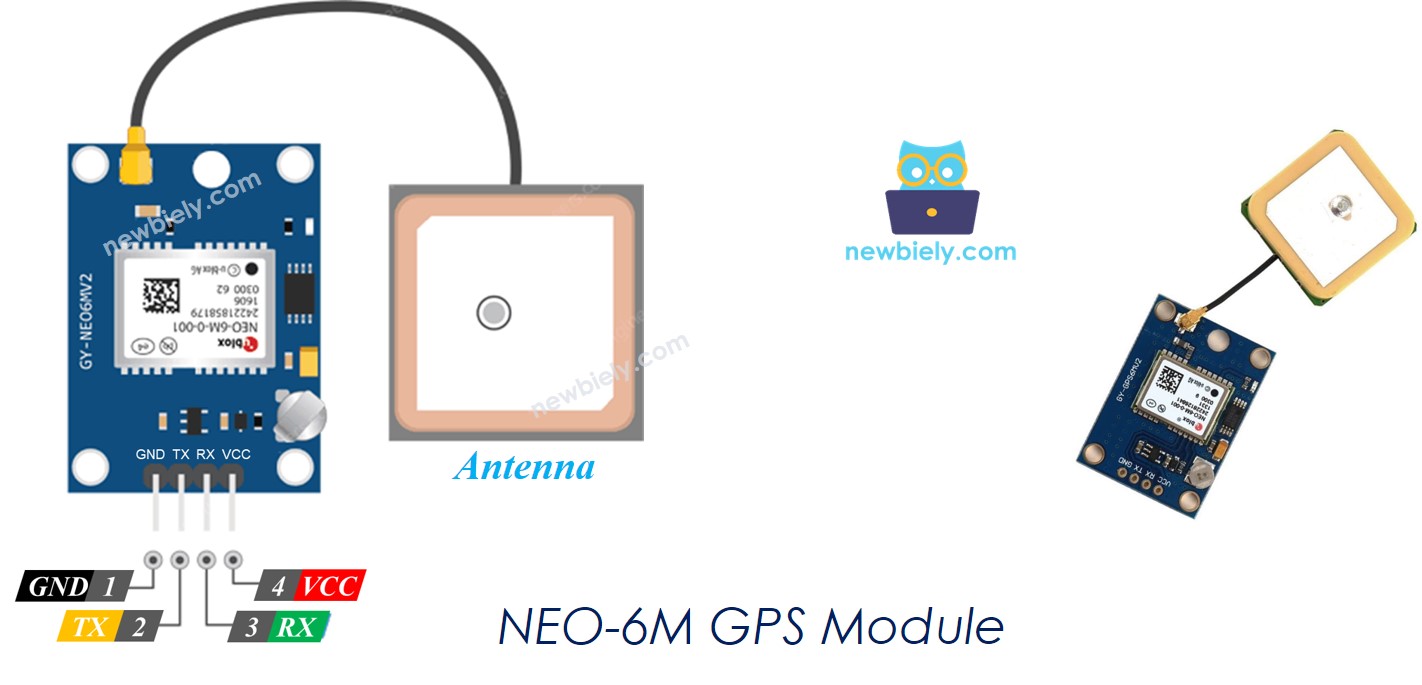
Diagramme de câblage
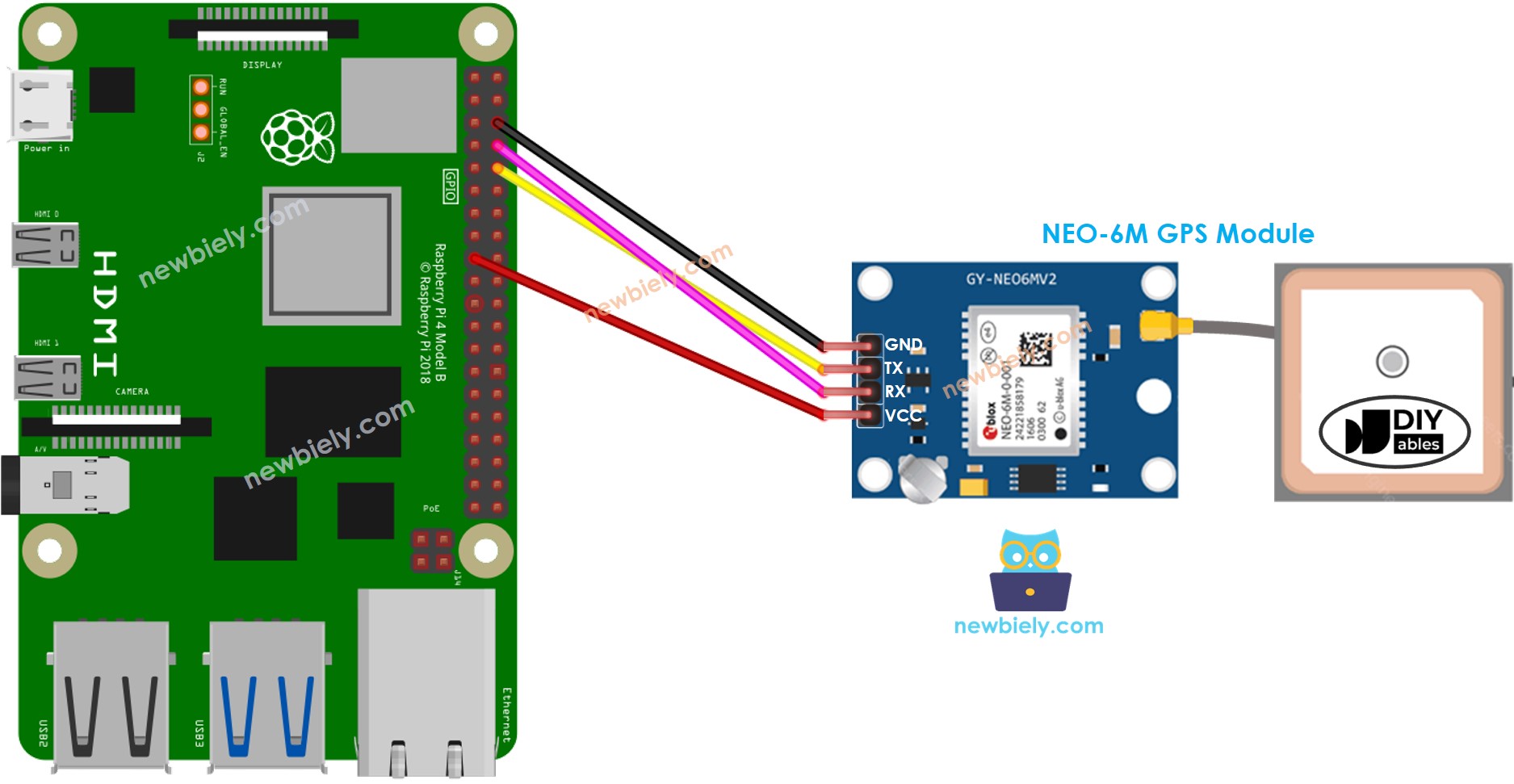
Cette image a été créée avec Fritzing. Cliquez pour agrandir l'image.
Pour simplifier et organiser votre montage de câblage, nous recommandons l'utilisation d'un shield à bornier à vis pour Raspberry Pi. Ce shield assure des connexions plus sûres et mieux gérées, comme illustré ci-dessous :
Code Raspberry Pi
Lecture des coordonnées GPS, de la vitesse (km/h) et de la date et de l'heure
Étapes rapides
- Assurez-vous d'avoir Raspbian ou tout autre système d'exploitation compatible avec Raspberry Pi installé sur votre Pi.
- Assurez-vous que votre Raspberry Pi est connecté au même réseau local que votre PC.
- Assurez-vous que votre Raspberry Pi est connecté à Internet si vous avez besoin d'installer certaines bibliothèques.
- Si c'est la première fois que vous utilisez Raspberry Pi, consultez Installation du logiciel - Raspberry Pi..
- Connectez votre PC au Raspberry Pi via SSH en utilisant le client SSH intégré sur Linux et macOS ou PuTTY sur Windows. Consultez comment connecter votre PC au Raspberry Pi via SSH.
- Assurez-vous d'avoir la bibliothèque RPi.GPIO installée. Sinon, installez-la en utilisant la commande suivante :
- Activez l'interface série sur le Raspberry Pi en suivant les instructions sur Raspberry Pi - comment activer l'interface série
- Installez la bibliothèque pyserial pour la communication avec le module GPS :
- Créez un fichier script Python gps.py et ajoutez le code suivant :
- Enregistrez le fichier et exécutez le script Python en entrant la commande suivante dans le terminal :
- Consultez le résultat sur le Terminal.
Le script s'exécute en boucle infinie en continu jusqu'à ce que vous appuyiez sur Ctrl + C dans le terminal.
Calculer la distance entre l'emplacement actuel et un emplacement prédéfini
Le code ci-dessous calcule la distance entre l'emplacement actuel et Londres (latitude : 51.508131, longitude : -0.128002).
Étapes rapides
- Installez la bibliothèque geopy pour le calcul des distances :
- Créez un fichier de script Python gps_distance.py et ajoutez le code suivant :
- Enregistrez le fichier et exécutez le script Python en exécutant la commande suivante dans le terminal :
- Consultez le résultat sur le Terminal.
