Raspberry Pi - RFID - Servomoteur
Ce didacticiel vous explique comment utiliser un Raspberry Pi et un module RFID NFC RC522 pour contrôler un servomoteur. Le processus fonctionne comme suit :
- Lorsqu'une étiquette autorisée est présentée, le Raspberry Pi fera pivoter le servomoteur à 90°.
- Si la même étiquette autorisée est présentée à nouveau, le Raspberry Pi fera revenir le servomoteur à 0°.
- Ce cycle se répétera continuellement.
Cela peut être utilisé pour sécuriser une armoire, un tiroir, une porte, ou pour ouvrir et fermer une mangeoire pour animaux...
Préparation du matériel
Ou vous pouvez acheter les kits suivants:
| 1 | × | Kit de Capteurs DIYables (30 capteurs/écrans) | |
| 1 | × | Kit de Capteurs DIYables (18 capteurs/écrans) |
À propos du module RFID/NFC RC522 et du servomoteur
Si vous n'êtes pas familier avec le module RFID/NFC RC522 et le servomoteur (y compris le brochage, le fonctionnement et la programmation), les tutoriels suivants peuvent fournir plus d'informations :
- Raspberry Pi - RFID. tutorial
- Raspberry Pi - Moteur Servo. tutorial
Comment ça marche
- Les UIDs de certaines étiquettes RFID/NFC sont programmés dans le code du Raspberry Pi.
- Lorsque l'utilisateur passe une étiquette RFID/NFC sur le lecteur RFID/NFC, le lecteur lit l'UID de l'étiquette.
- Le Raspberry Pi récupère ensuite l'UID du lecteur et le compare aux UIDs prédéfinis.
- Si l'UID correspond à l'un des UIDs prédéfinis, le Raspberry Pi contrôlera le servomoteur à 90°.
- Si l'étiquette est de nouveau passée, le Raspberry Pi contrôlera le servomoteur à 0°.
- Ce processus se répète en continu.
Diagramme de câblage
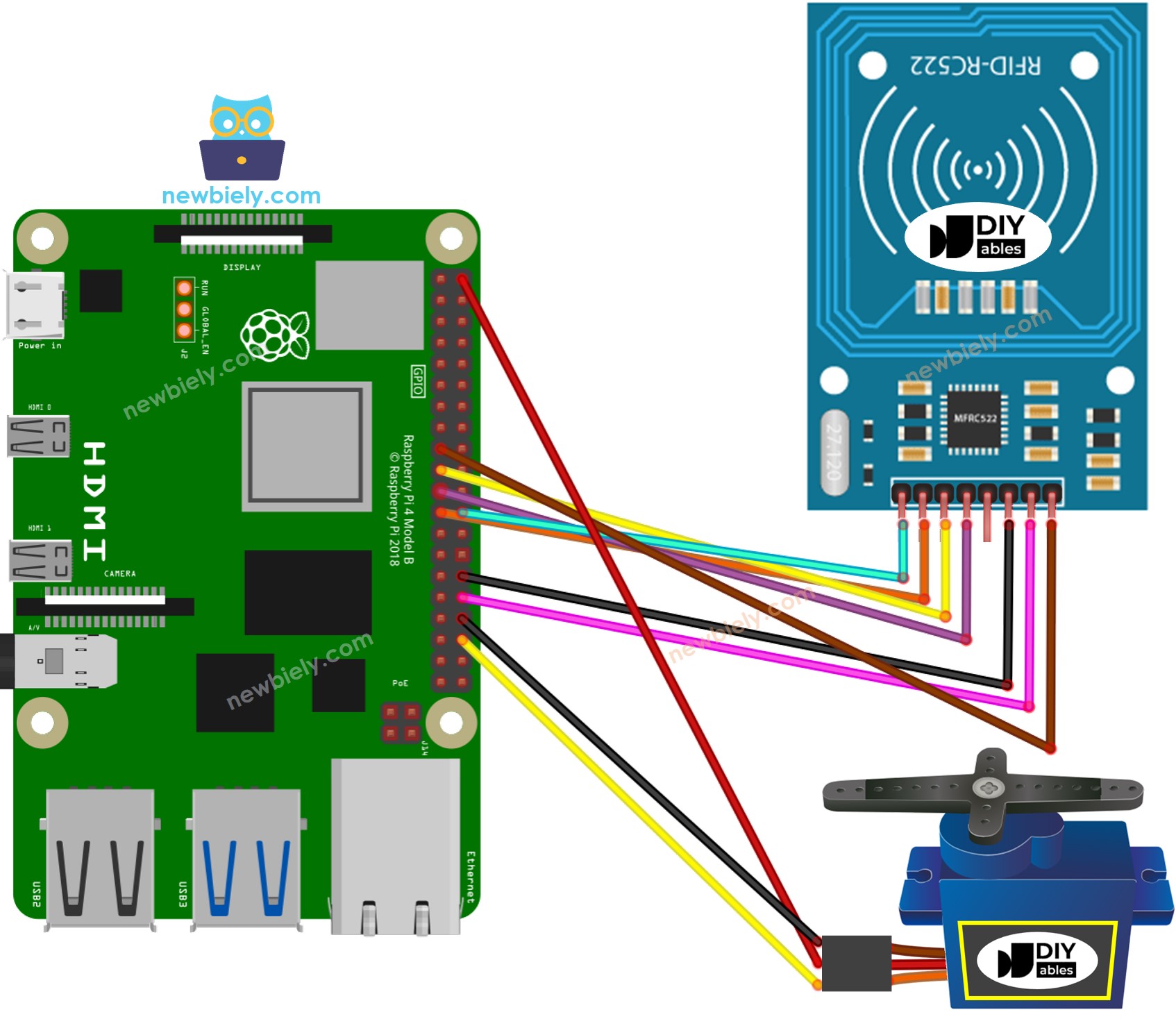
Cette image a été créée avec Fritzing. Cliquez pour agrandir l'image.
Pour simplifier et organiser votre montage de câblage, nous recommandons l'utilisation d'un shield à bornier à vis pour Raspberry Pi. Ce shield assure des connexions plus sûres et mieux gérées, comme illustré ci-dessous :
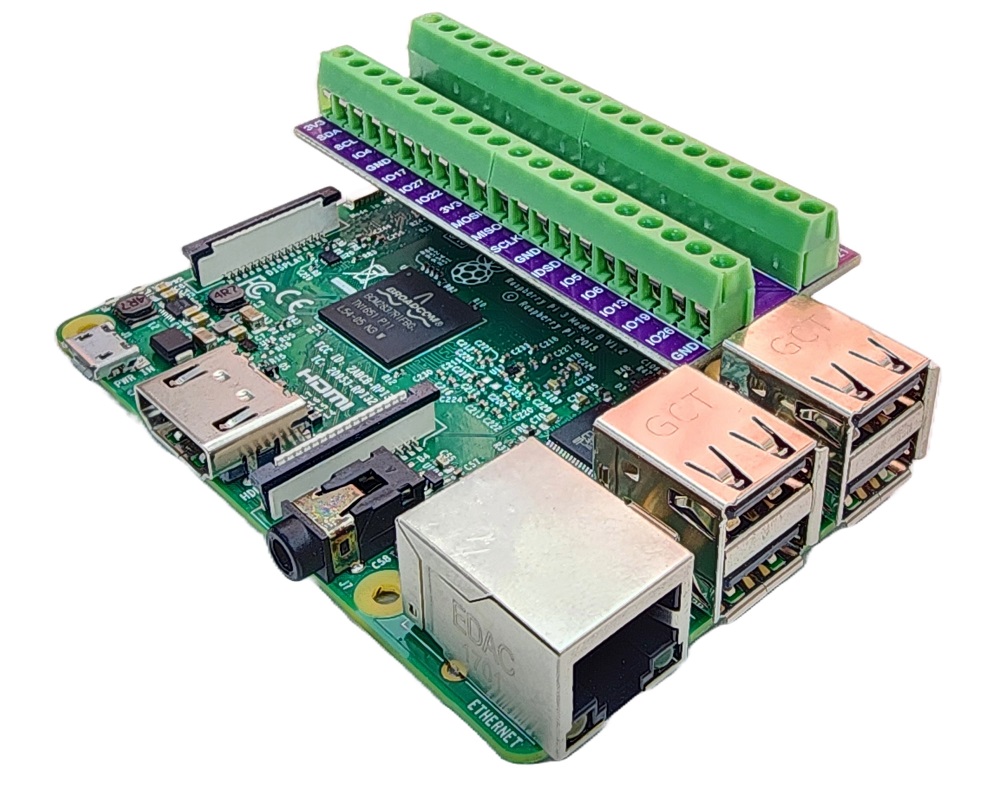
Dans le schéma de câblage ci-dessus, un adaptateur 5V est utilisé pour alimenter le Raspberry Pi, le servo-moteur et le module RC522 indirectement via la broche 3.3V du Raspberry Pi.
※ Note:
La disposition des broches peut varier selon le fabricant. Utilisez TOUJOURS les étiquettes imprimées sur le module. L'image ci-dessus affiche le brochage des modules du fabricant DIYables.
Pour des raisons de simplicité, le schéma de câblage ci-dessus est utilisé à des fins de test ou d'éducation, et pour un servomoteur avec un faible couple. Nous vous recommandons vivement d'utiliser une source d'alimentation externe pour le servomoteur en pratique. Consultez comment fournir une alimentation externe pour le servomoteur dans le tutoriel Raspberry Pi - Moteur Servo..
Tableau de câblage du module RFID/NFC RC522
| RFID/NFC RC522 | Raspberry Pi |
|---|---|
| SS | → GPIO 8 (SPI0 CS) |
| SCK | → GPIO 11 (SPI0 SCL) |
| MOSI | → GPIO 10 (SPI0 MOSI) |
| MISO | → GPIO 9 (SPI0 MISO) |
| IRQ | not connected |
| GND | → Any GND Pin |
| RST | → Pin 31 (GPIO12) |
| VCC | → Pin 1 or Pin 16 (3.3V) |
Tableau de câblage du servomoteur
| Servo Motor | Arduino | 5V DC Adapter |
|---|---|---|
| VCC (red) | → positive | |
| GND (brown) | → negative | |
| SIG (yellow) | → A5 |
Tableau de câblage de l'adaptateur 5V DC
| 5V DC Adapter | Servo Motor | Raspberry Pi |
|---|---|---|
| Positive | → VCC | |
| Positive | -> Vin | |
| Negative | → GND | |
| Negative | → GND |
Code Raspberry Pi - Tag RFID/NFC Unique
Étapes rapides
- Assurez-vous d'avoir Raspbian ou un autre système d'exploitation compatible avec Raspberry Pi installé sur votre Pi.
- Assurez-vous que votre Raspberry Pi est connecté au même réseau local que votre PC.
- Assurez-vous que votre Raspberry Pi est connecté à Internet si vous devez installer des bibliothèques.
- Si c'est la première fois que vous utilisez Raspberry Pi, voyez Installation du logiciel - Raspberry Pi.
- Connectez votre PC au Raspberry Pi via SSH en utilisant le client SSH intégré sur Linux et macOS ou PuTTY sur Windows. Voir comment connecter votre PC au Raspberry Pi via SSH.
- Assurez-vous que vous avez la bibliothèque RPi.GPIO installée. Sinon, installez-la en utilisant la commande suivante :
- Activez l'interface SPI sur Raspberry Pi en suivant les instructions sur Raspberry Pi - comment activer l'interface SPI
- Assurez-vous que la bibliothèque spidev est installée. Sinon, installez-la en utilisant la commande suivante :
- Assurez-vous d'avoir la bibliothèque mfrc522 installée. Sinon, installez-la en utilisant la commande suivante :
- Créez un fichier script Python rfid_servo.py et ajoutez le code suivant :
- Enregistrez le fichier et exécutez le script Python en entrant la commande suivante dans le terminal :
Le script s'exécute dans une boucle infinie continuellement jusqu'à ce que vous appuyiez sur Ctrl + C dans le terminal.
Pour identifier l'UID d'une étiquette RFID/NFC, appuyez une étiquette RFID/NFC sur le module RFID-RC522. L'UID peut être vu sur le Terminal.
Une fois que vous avez votre UID :
- Remplacez la ligne 20 du code par l'UID, par exemple byte authorizedUID[4] = {0x3A, 0xC9, 0x6A, 0xCB};
- Exécutez à nouveau le script Python
- Placez une étiquette RFID/NFC sur le module RFID-RC522
- Le servomoteur tournera à 90°
- Vérifiez la sortie sur le Terminal
- Touchez à nouveau le même tag RFID/NFC utilisé sur le module RFID-RC522.
- Regardez le servomoteur pivoter à 0°.
- Consultez la sortie sur le Terminal.
- Approchez un tag RFID ou NFC du module RFID-RC522.
- Vérifiez la sortie sur le Terminal.
