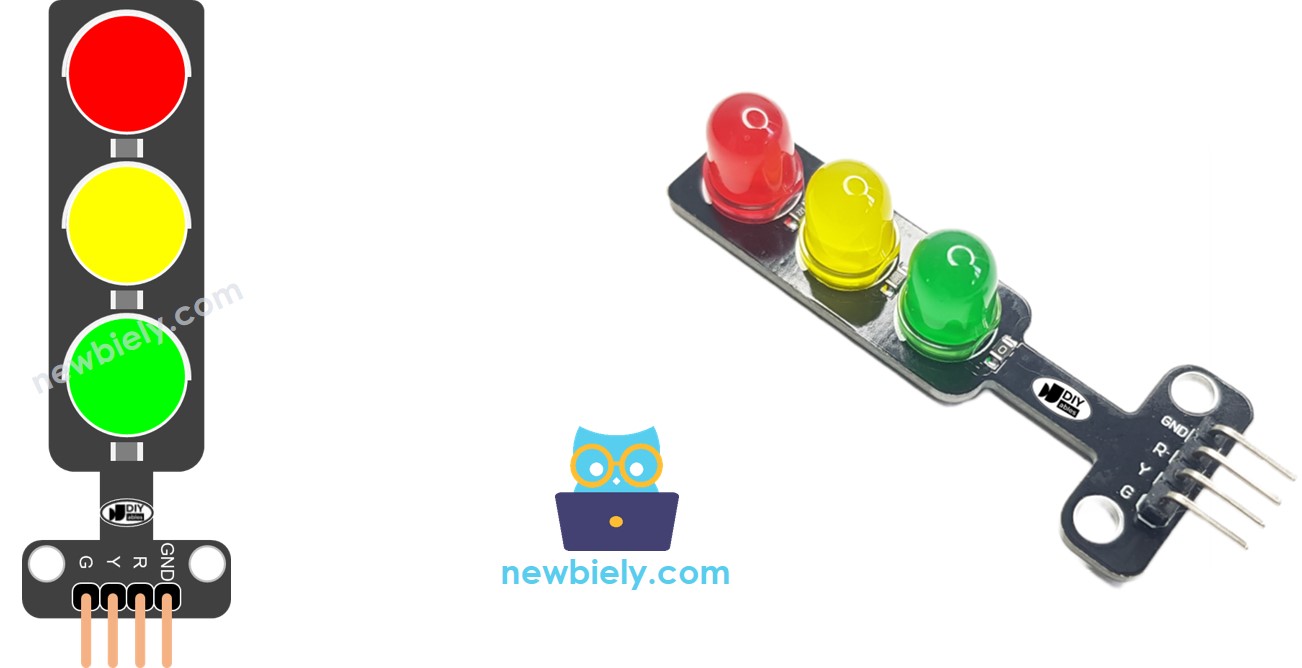
Arduino Nano - Feu de circulation
Ce tutoriel vous explique comment utiliser un Arduino Nano pour contrôler un module de feu de circulation. Plus précisément, nous aborderons les aspects suivants :
Établir la connexion entre le module de feu de circulation et l'Arduino Nano
Programmer l'Arduino Nano pour superviser le module de feu de circulation RGB
Implémenter la programmation de l'Arduino Nano pour réguler le module de feu de circulation RGB sans dépendre de la fonction delay().
Ou vous pouvez acheter les kits suivants:
Divulgation : Certains des liens fournis dans cette section sont des liens affiliés Amazon. Nous pouvons recevoir une commission pour tout achat effectué via ces liens, sans coût supplémentaire pour vous. Nous vous remercions de votre soutien.
Un module de feu de circulation comprend quatre broches :
Broche GND : Connectez cette broche au GND de l'Arduino Nano.
Broche R : Contrôle la lumière rouge ; connectez cette broche à une sortie numérique de l'Arduino Nano.
Broche Y : Gère la lumière jaune ; connectez cette broche à une sortie numérique de l'Arduino Nano.
Broche G : Régit la lumière verte ; connectez cette broche à une sortie numérique de l'Arduino Nano.
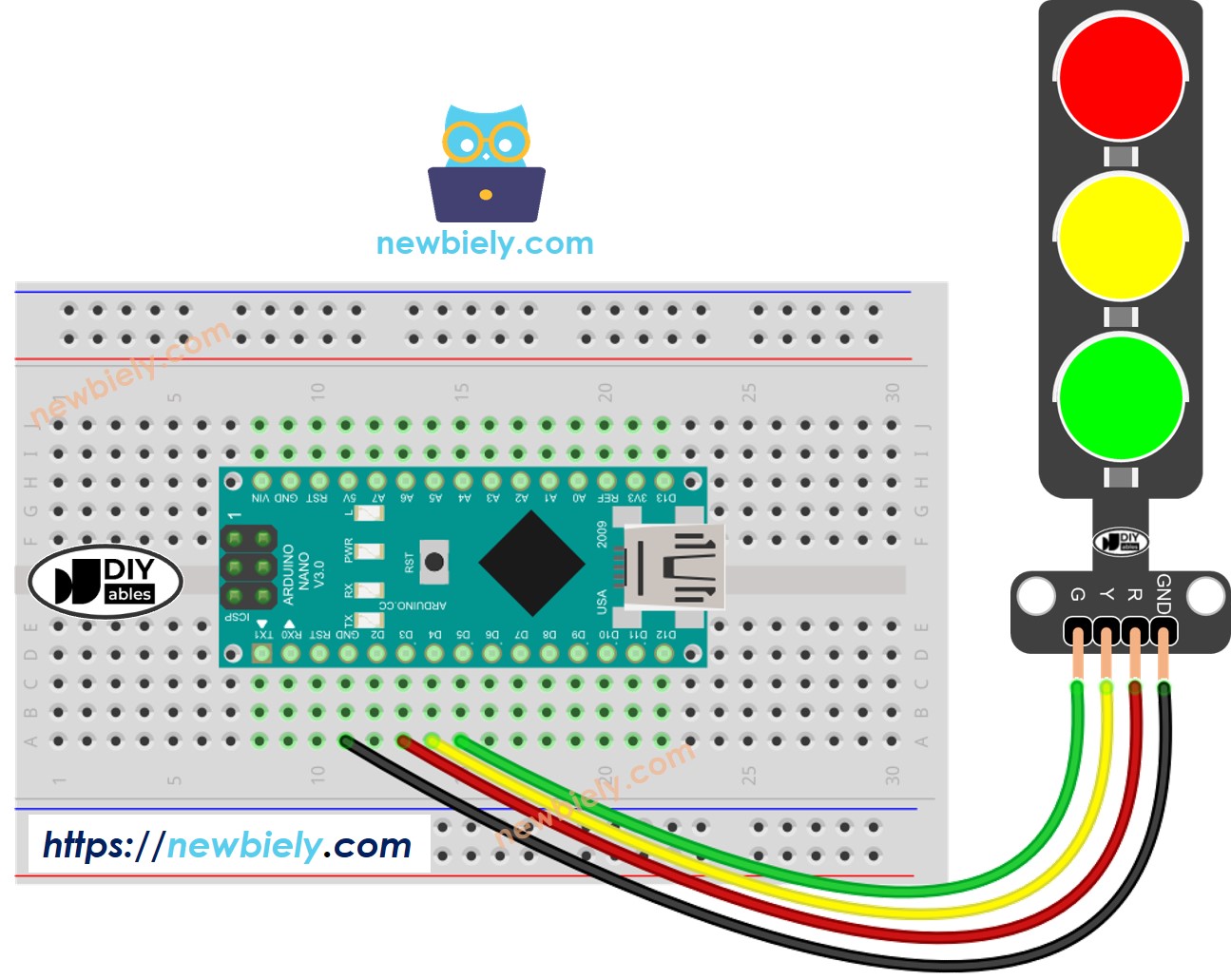
Cette image a été créée avec Fritzing. Cliquez pour agrandir l'image.
Voir Comment alimenter un Arduino Nano..
#define PIN_RED 3
#define PIN_YELLOW 4
#define PIN_GREEN 5
#define RED_TIME 4000
#define YELLOW_TIME 4000
#define GREEN_TIME 4000
void setup() {
pinMode(PIN_RED, OUTPUT);
pinMode(PIN_YELLOW, OUTPUT);
pinMode(PIN_GREEN, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(PIN_RED, HIGH);
digitalWrite(PIN_YELLOW, LOW);
digitalWrite(PIN_GREEN, LOW);
delay(RED_TIME);
digitalWrite(PIN_RED, LOW);
digitalWrite(PIN_YELLOW, HIGH);
digitalWrite(PIN_GREEN, LOW);
delay(YELLOW_TIME);
digitalWrite(PIN_RED, LOW);
digitalWrite(PIN_YELLOW, LOW);
digitalWrite(PIN_GREEN, HIGH);
delay(GREEN_TIME);
}
Copiez le code ci-dessus et ouvrez-le avec Arduino IDE
Cliquez sur le bouton Upload dans Arduino IDE pour téléverser le code sur Arduino Nano
Examinez le module de feu de circulation
Il est important de noter que le fonctionnement exact d'un feu de circulation peut varier en fonction de la conception spécifique et de la technologie utilisée dans différentes régions et intersections. Les principes décrits ci-dessus offrent une compréhension générale du fonctionnement des feux de circulation pour gérer le trafic et améliorer la sécurité sur les routes.
Le code ci-dessus démontre le contrôle individuel des lumières. Maintenant, améliorons le code pour une meilleure optimisation.
#define PIN_RED 3
#define PIN_YELLOW 4
#define PIN_GREEN 5
#define RED_TIME 2000
#define YELLOW_TIME 1000
#define GREEN_TIME 2000
#define RED 0
#define YELLOW 1
#define GREEN 2
const int pins[] = { PIN_RED, PIN_YELLOW, PIN_GREEN };
const int times[] = { RED_TIME, YELLOW_TIME, GREEN_TIME };
void setup() {
pinMode(PIN_RED, OUTPUT);
pinMode(PIN_YELLOW, OUTPUT);
pinMode(PIN_GREEN, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
trafic_light_on(RED);
delay(times[RED]);
trafic_light_on(YELLOW);
delay(times[YELLOW]);
trafic_light_on(GREEN);
delay(times[GREEN]);
}
void trafic_light_on(int light) {
for (int i = RED; i <= GREEN; i++) {
if (i == light)
digitalWrite(pins[i], HIGH);
else
digitalWrite(pins[i], LOW);
}
}
#define PIN_RED 3
#define PIN_YELLOW 4
#define PIN_GREEN 5
#define RED_TIME 2000
#define YELLOW_TIME 1000
#define GREEN_TIME 2000
#define RED 0
#define YELLOW 1
#define GREEN 2
const int pins[] = {PIN_RED, PIN_YELLOW, PIN_GREEN};
const int times[] = {RED_TIME, YELLOW_TIME, GREEN_TIME};
void setup() {
pinMode(PIN_RED, OUTPUT);
pinMode(PIN_YELLOW, OUTPUT);
pinMode(PIN_GREEN, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
for (int light = RED; light <= GREEN; light ++) {
trafic_light_on(light);
delay(times[light]);
}
}
void trafic_light_on(int light) {
for (int i = RED; i <= GREEN; i ++) {
if (i == light)
digitalWrite(pins[i], HIGH);
else
digitalWrite(pins[i], LOW);
}
}
#define PIN_RED 3
#define PIN_YELLOW 4
#define PIN_GREEN 5
#define RED_TIME 2000
#define YELLOW_TIME 1000
#define GREEN_TIME 2000
#define RED 0
#define YELLOW 1
#define GREEN 2
const int pins[] = { PIN_RED, PIN_YELLOW, PIN_GREEN };
const int times[] = { RED_TIME, YELLOW_TIME, GREEN_TIME };
unsigned long last_time = 0;
int light = RED;
void setup() {
pinMode(PIN_RED, OUTPUT);
pinMode(PIN_YELLOW, OUTPUT);
pinMode(PIN_GREEN, OUTPUT);
trafic_light_on(light);
last_time = millis();
}
void loop() {
if ((millis() - last_time) > times[light]) {
light++;
if (light >= 3)
light = RED;
trafic_light_on(light);
last_time = millis();
}
}
void trafic_light_on(int light) {
for (int i = RED; i <= GREEN; i++) {
if (i == light)
digitalWrite(pins[i], HIGH);
else
digitalWrite(pins[i], LOW);
}
}
※ NOS MESSAGES
N'hésitez pas à partager le lien de ce tutoriel. Cependant, veuillez ne pas utiliser notre contenu sur d'autres sites web. Nous avons investi beaucoup d'efforts et de temps pour créer ce contenu, veuillez respecter notre travail !


