Arduino Nano - Plusieurs boutons
Ce tutoriel vous apprend à programmer un Arduino Nano afin qu'il puisse gérer plusieurs boutons en même temps sans dépendre de la fonction delay(). Le tutoriel propose du code de deux manières différentes :
- Code Arduino Nano pour gérer plusieurs boutons avec anti-rebond.
- Code Arduino Nano pour gérer plusieurs boutons avec anti-rebond en utilisant des tableaux.
Nous utiliserons quatre boutons comme exemples. Vous pouvez facilement les modifier pour les adapter à deux boutons, trois boutons, cinq boutons ou même plus.
Préparation du matériel
Ou vous pouvez acheter les kits suivants:
| 1 | × | Kit de Capteurs DIYables (30 capteurs/écrans) | |
| 1 | × | Kit de Capteurs DIYables (18 capteurs/écrans) |
À propos du bouton
Si vous n'êtes pas familier avec le bouton (brochage, fonctionnement, programmation...), les tutoriels suivants peuvent vous fournir plus d'informations :
- Arduino Nano - Bouton. tutorial
- Arduino Nano - Bouton - Anti-rebond. tutorial
Diagramme de câblage
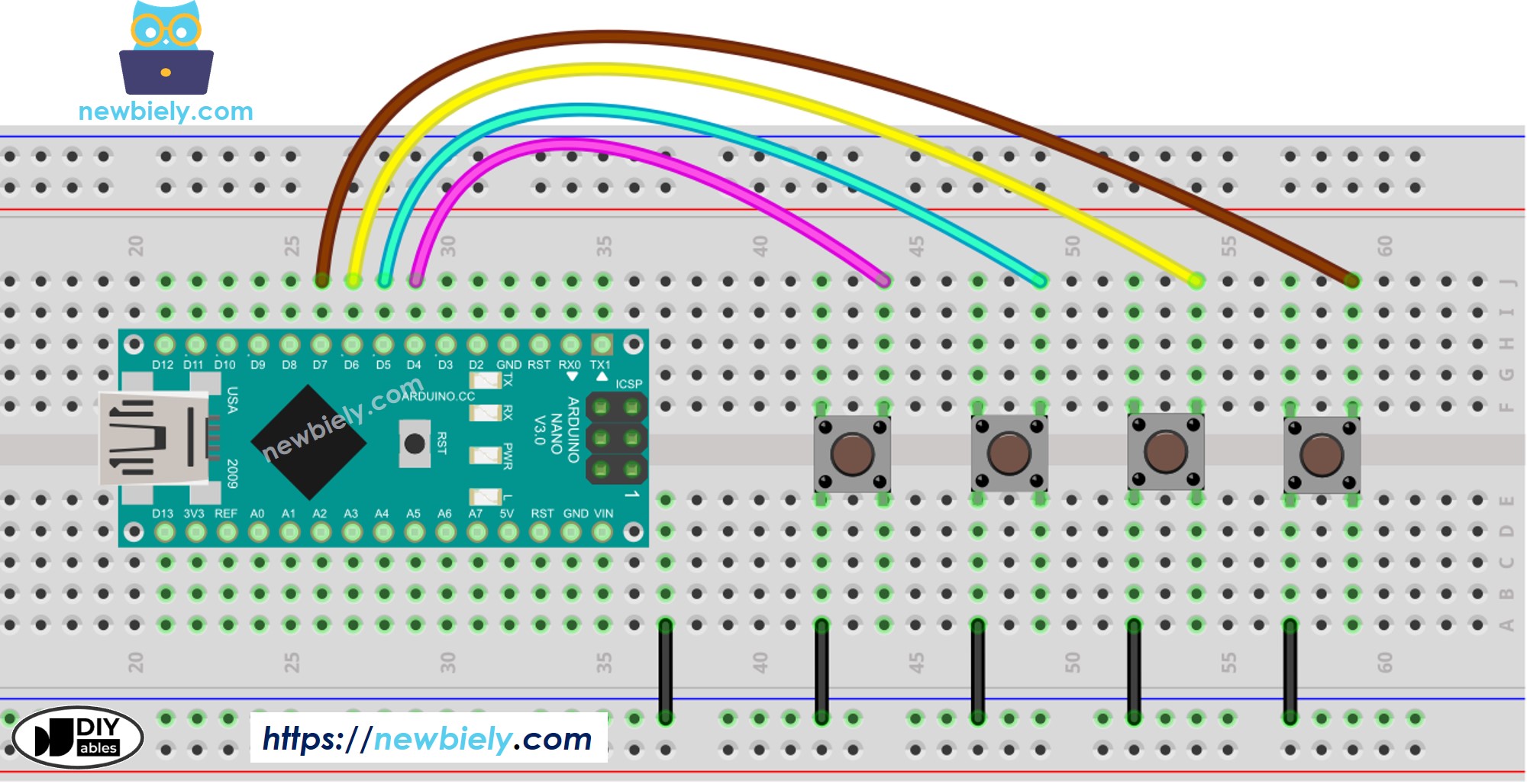
Cette image a été créée avec Fritzing. Cliquez pour agrandir l'image.
Code Arduino Nano - Plusieurs boutons avec anti-rebond
Lors de l'utilisation de plusieurs boutons, les choses peuvent se compliquer dans certains scénarios :
- Applications nécessitant un anti-rebond pour les boutons (voir pourquoi nous avons besoin de débouncer pour les boutons)
- Applications nécessitant de détecter les changements d'état (appuyé/libéré)
Heureusement, la bibliothèque ezButton simplifie ce processus en gérant en interne les rebonds et les événements de bouton. Cela décharge les utilisateurs de la tâche de gestion des horodatages et des variables lors de l'utilisation de la bibliothèque. De plus, l'utilisation d'un tableau de boutons peut améliorer la clarté et la concision du code.
Étapes rapides
- Faites le câblage comme sur l'image ci-dessus.
- Connectez la carte Arduino Nano à votre PC via un câble USB.
- Ouvrez l'IDE Arduino sur votre PC.
- Sélectionnez la bonne carte Arduino Nano (par exemple, Arduino Nano Uno) et le port COM.
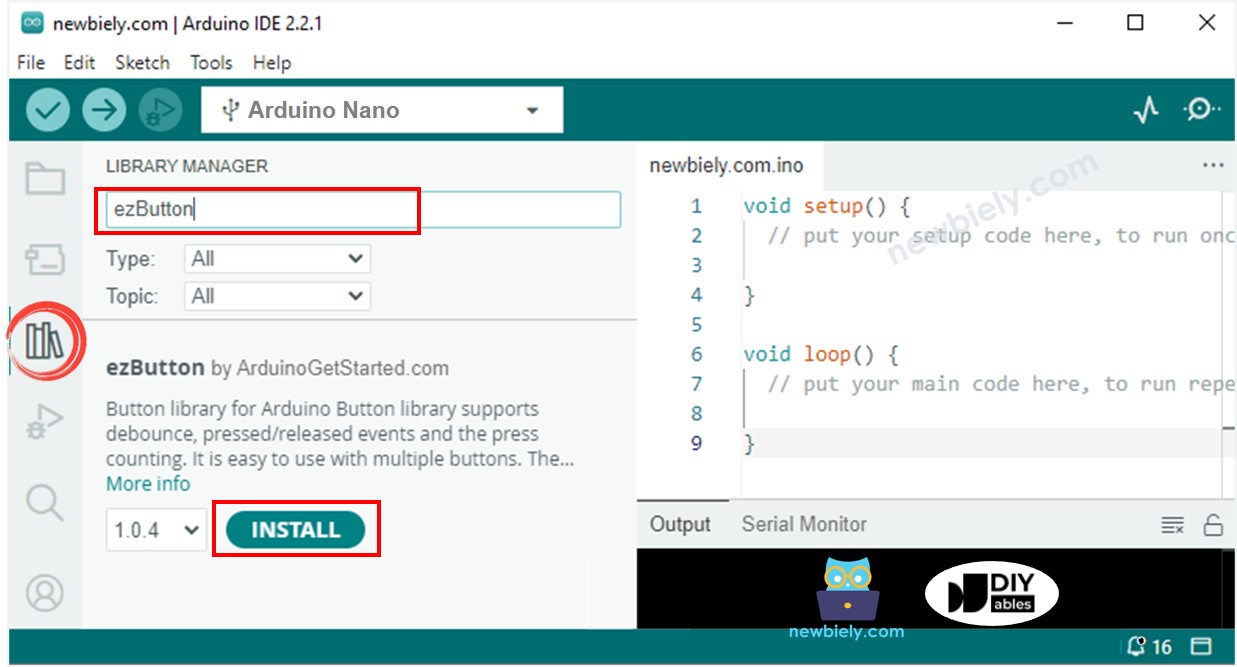
- Cliquez sur l'icône des Libraries dans la barre de gauche de l'IDE Arduino.
- Recherchez "ezButton", puis trouvez la bibliothèque de bouton par Arduino NanoGetStarted.
- Cliquez sur le bouton Install pour installer la bibliothèque ezButton.
- Copiez le code ci-dessus et collez-le dans l'IDE Arduino.
- Compilez et téléchargez le code sur la carte Arduino Nano en cliquant sur le bouton Upload dans l'IDE Arduino.
- Ouvrez le moniteur série sur Arduino IDE
- Appuyez et relâchez le bouton un par un
Code Arduino Nano - Plusieurs boutons utilisant un tableau
Nous pouvons améliorer le code ci-dessus en utilisant un tableau de boutons. Le code suivant utilise ce tableau pour gérer les objets boutons.
